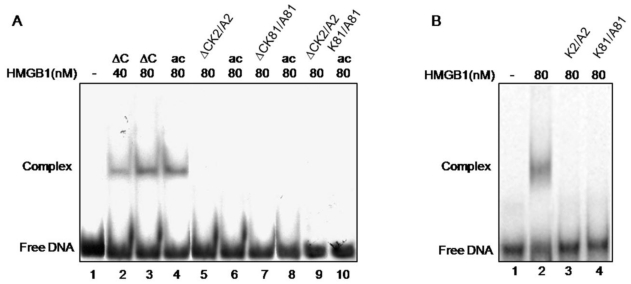
Fig 4.
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay of the binding of various HMGB1 proteins to cisplatin-damaged DNA. Panel A. Interaction of wild-type tailless (∆C) protein (lanes 2 and 3), in vitro acetylated ∆C at K2 (lane 4), ∆CK2/A2 mutant (lane 5), acetylated ∆CK2/A2 mutant (lane 6), ∆C K81/A81 mutant (lane 7), acetylated ∆CK81/A81 mutant (lane 8), ∆ K2/A2,K81/A81 double mutant (lane 9) and acetylated ∆CK2/A2K81/A81 mutant (lane 10). Lane 1 shows the position of free DNA. Panel B. Interaction of full-length HMGB1 (lane 2) and HMGB1K2/A2 and HMGB1K81/A81 mutants (lanes 3 and 4 respectively) with cis-platinated DNA. Lane 1 shows the position of free DNA.