Table 1.
Initial studies and condition optimizationa.
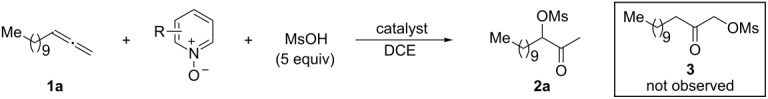 | ||||
| Entry | Catalyst (5 mol %) | N-Oxide (2 equiv) | Reaction conditions | Yieldb (%) |
| 1 | Ph3PAuNTf2 | pyridine N-oxide | rt, 2 d | 46 |
| 2 | Ph3PAuNTf2 | pyridine N-oxide | 40 °C, 8 h | 52 |
| 3 | Ph3PAuNTf2 | quinoline N-oxide | 40 °C, 8 h | 51/6c |
| 4 | Ph3PAuNTf2 | 2-bromopyridine N-oxide | 40 °C, 8 h | 44/10c |
| 5 | Ph3PAuNTf2 | 3,5-dichloropyridine N-oxide | 40 °C, 8 h | 75 |
| 6 | IPrAuNTf2 | 3,5-dichloropyridine N-oxide | 40 °C, 8 h | 10/53c |
| 7 | Cy-JohnPhosAuNTf2 | 3,5-dichloropyridine N-oxide | 40 °C, 8 h | 47/7c |
| 8 | (4-CF3Ph)3PAuNTf2 | 3,5-dichloropyridine N-oxide | 40 °C, 8 h | 80(77d) |
| 9e | (4-CF3Ph)3PAuNTf2 | 3,5-dichloropyridine N-oxide | 40 °C, 8 h | 55/13c |
| 10 | — | 3,5-dichloropyridine N-oxide | 40 °C, 8 h | — |
a[1a] = 0.05 M; bdetermined by 1H NMR using diethyl phthalate as the external standard; cunreacted starting material; disolated yield; e2.5 equiv of MsOH.
