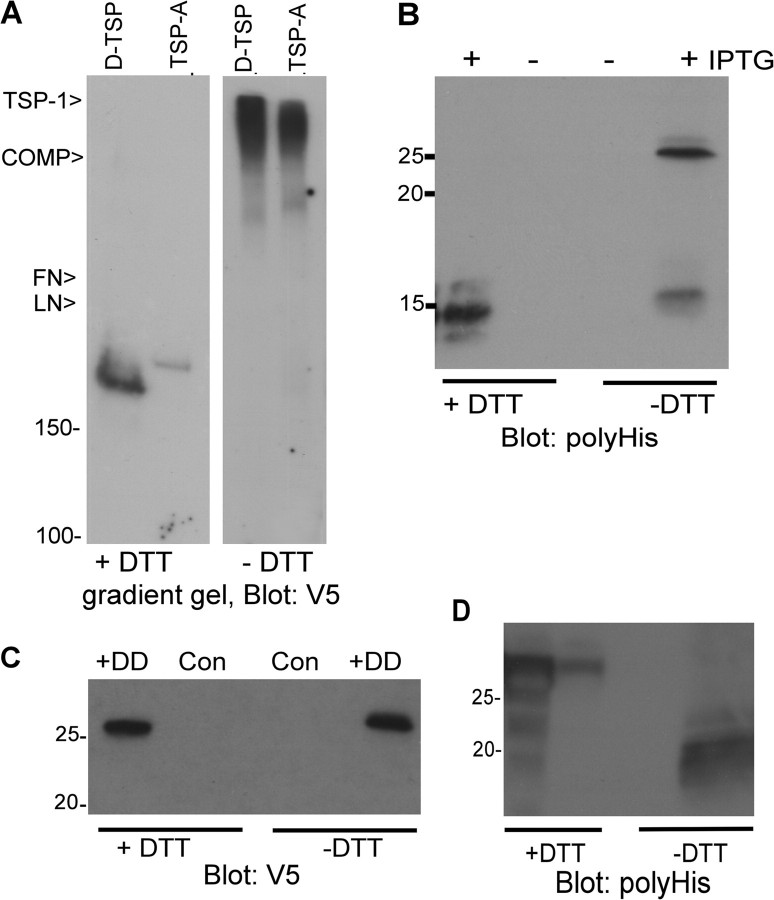
FIG. 3.
Oligomerization properties of Ciona TSP-A and TSP-DD. (A) Oligomerization of Ciona intestinalis TSP-A. TSP-A and Drosophila TSP were collected from conditioned media of transiently transfected COS-7 cells onto heparin–Sepharose, resolved on 4–10% polyacrylamide gradient gels under reducing or nonreducing conditions, and analyzed by immunoblotting. Migration positions of purified ECM glycoproteins used nonreduced as additional markers are shown to the left of the panel. (B) The IVR has independent dimerization activity. The 6His-tagged IVR of TSP-A was inducibly expressed in Escherichia coli, purified on metal affinity beads, resolved on 15% polyacrylamide gels under reducing or nonreducing conditions, and analyzed by immunoblotting. (C,D) The DD and CX2C domain of C. intestinalis TSP-DD lack oligomerization activity. Tagged versions of the discoidin domain (C) or CX2C domain (D) were collected from conditioned media of transiently transfected COS-7 cells (C) or bacterial lysates (D) onto metal affinity beads, resolved on 12.5% polyacrylamide gels under reducing or nonreducing conditions, and analyzed by immunoblotting.