Figure 1.
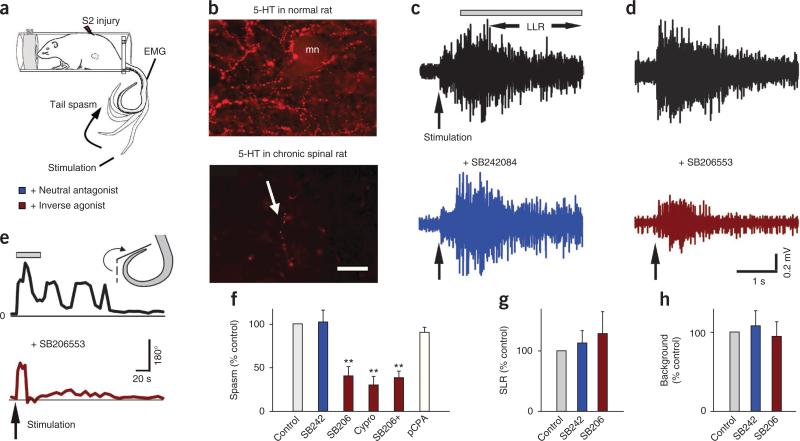
Constitutive 5-HT2 receptor activity, but not residual 5-HT, causes spasms. (a) Schematic of tail spasm in an awake chronic spinal rat with S2 sacral transection. (b) Representative immunofluorescence images of 5-HT fibers (beaded) in the S4 ventral horn of normal rats (top; mn, motoneuron, n = 5 rats) and chronic spinal rats (bottom; the arrow indicates a residual fiber, n = 5; scale bar, 50 μm). (c,d) Spasms in chronic spinal rat evoked by cutaneous electrical stimulation of the tail (pulse three times the threshold (3×T)) and recorded with EMG (quantified during the length of time indicated by the bar, LLR) before and after blocking effects of residual 5-HT with i.t. injection of the neutral antagonist SB242084 (3 mM in 30 μl saline). (d) Lack of spasm (LLR) after blocking constitutive receptor activity with the inverse agonist SB206553 (i.t., 3 mM in 30 μl saline). (e) Tail flexion angle during spasms before and after SB206553 injection, quantified during the length of time indicated by the bar. (f) Group means of spasms (normalized to predrug control) with SB242084 (abbreviated SB242; LLR), SB206553 (SB206 for LLR EMG recording; and SB206+ for tail-angle spasms) and cyproheptadine (cypro; LLR; 10 mg per kg body weight, orally), and after depletion of residual 5-HT with para-chlorophenylalanine-methylester (pCPA) (two 300 mg per kg body weight intraperitoneal injections over 48 h; tail-angle), with n = 5 rats per drug. (g,h) Normalized group means of SLR and background EMG with SB242084 and SB206553. **P < 0.01 relative to predrug control, 100%. Error bars indicate s.e.m.