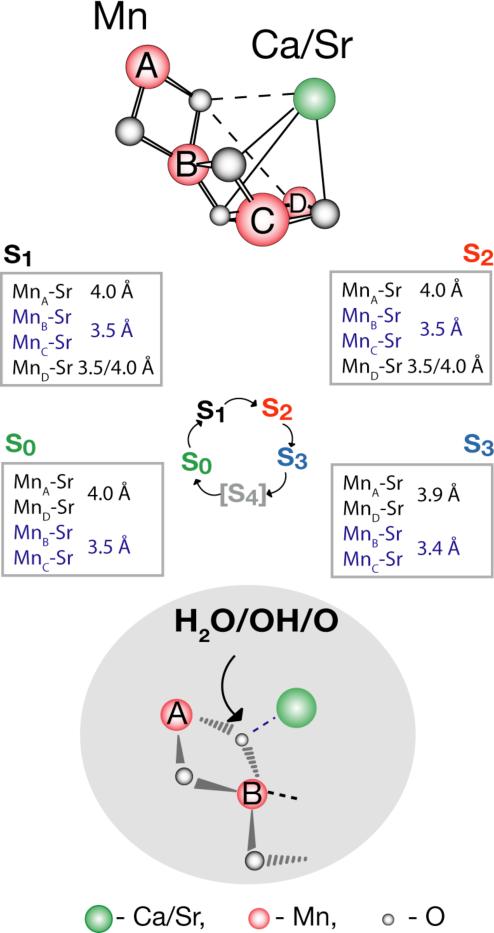
Figure 6.
Schematic of the structural changes accompanying the S-state transitions in the Mn4Ca(Sr) cluster is placed within the context of the recent structural model III from single-crystal X-ray spectroscopy. The critical transition is the S2 to S3 advancement, when the Mn-Mn di-μ-oxo bridge distances of the Mn4-core become elongated from ~2.7-2.8 Å to ~2.8-2.9 Å. Simultaneously, Sr is drawn closer to the Mn core with the Sr-Mn interaction at ~3.5 Å shortening to ~3.4 Å and at ~4.0 Å distance decreasing to 3.94 Å. We propose that this change is triggered by the ligand-centered oxidation of the oxygen atom that bridges the Mn with the Ca atoms. The Ca(Sr)-Mn distances in all the S-states are indicated in the boxes next to the S-states. Changes in the Mn-Mn and Ca(Sr)-Mn distances may be triggered by changes at an oxo-bridge. The oxo bridge between MnA, MnB may also bridge to Ca and possiblly to MnD as shown by dotted lines. It may therefore fulfill the critical function in the O-O formation chemistry consistent with earlier proposals by Kulik and coworkers [51] and Siegbahn [52].