Figure 2.
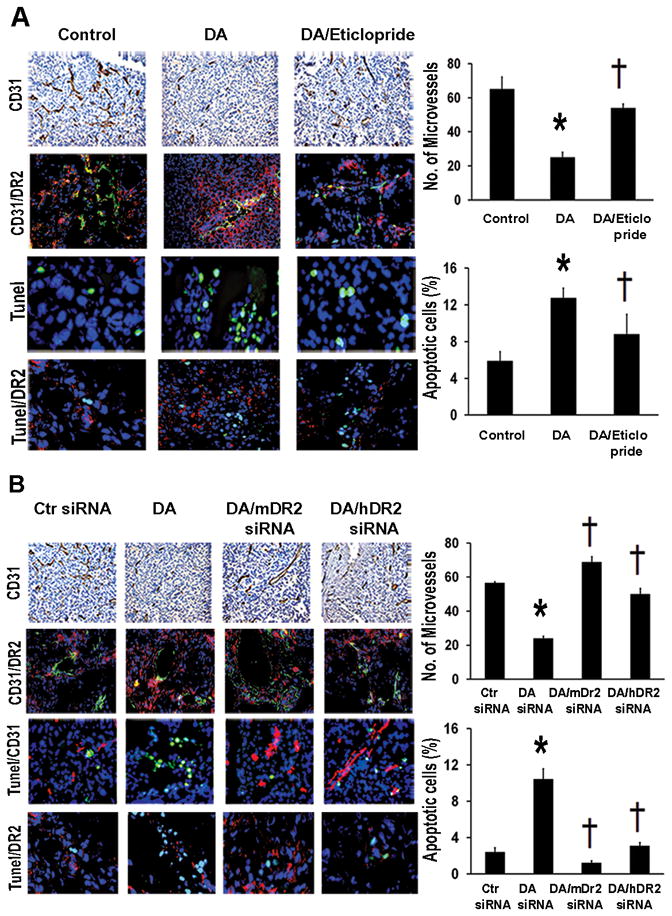
Dopamine decreases stress-stimulated angiogenesis and stimulates tumor cell apoptosis via its DR2. (A) MVD was significantly decreased by DA-treatment in SKOV3ip1-tumor tissues of stressed mice (*p<0.01). DA/eticlopride treatment significantly (†p<0.01) reversed DA-inhibitory effect on MVD. MVD was evaluated by immunohistochemical analysis of CD31 (DAB-staining). Microvessels were counted in five fields at 100X of each tissue sample (n=5). Values are means ± SE. DA treatment caused significantly (*p<0.005) higher apoptotic rates compared to control mice. This effect was also significantly († p< 0.005) reversed by DA/eticlopride combined treatment. Confocal images (200X) showing colocalization of DR2 (red fluorescence) in CD31-positive tumor endothelial cells (green fluorescence). Apoptotic cells (green fluorescence) were detected by Tunel staining (Promega kit). Percentages of apoptotic cells were calculated in five fields at 200X of each tissue sample (n=5). Values are means ± SE. Detection of DR2 (red fluorescence) in tumor apoptotic cells (green fluorescence) (Confocal images 200X). (B) DA/mDR2-siRNA and DA/hDR2-siRNA-CH combined treatments induced significant increase (†p <0.005) in MVD in stressed mice, reverting the DA-inhibitory effect on MVD (*p<0.005). Values are means ± SE. Detection of DR2 (red fluorescence) in tumor CD31-positive endothelial cells (green fluorescence) (Confocal images 200X). DA-stimulatory effect on tumor cell apoptosis was also significantly abrogated by the DA/mDR2-siRNA and DA/hDR2-siRNA treatments (†p <0.005). Values are means ± SE. Confocal images (200X) revealing colocalization of DR2 (red fluorescence) in tumor apoptotic cells (green fluorescence).
