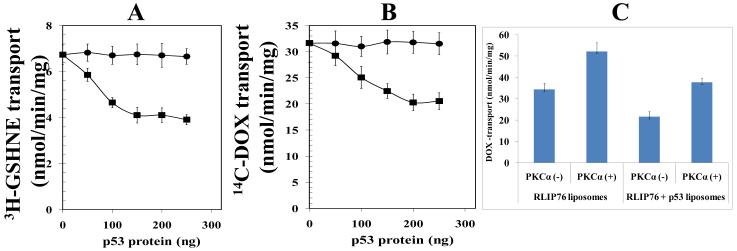
Figure 3.
Effect of p53 and PKCα on the transport-activity of RLIP76 The transport-activity of RLIP76 towards GS-HNE (panel A) and DOX (panel B) was measured by using purified rec-RLIP76 reconstituted into artificial cholesterol/asolectin liposomes as previously described (24). The effect of p53 (squares) or bovine albumin serum (round dots) at varying molar ratios was examined by incubating varying concentrations of these proteins in the transport medium. Transport medium contained RLIP76-proteoliposomes (250 ng protein/30 μL reaction-mixture), 10 μM 3H-GSHNE (specific activity 3.1 × 104 cpm/nmol) or 3.6 μM 14C-DOX (specific activity 8.5 × 104 cpm/nmol), without or with 4 mM ATP (three experiments, each in triplicate; n = 9). Heat-inactivated p53 protein was also used for additional control. The effect of p53 on PKCα-stimulated 14C-DOX transport-activity of RLIP76 was also performed (panel C). RLIP76-liposomes alone or in combination with p53-liposomes were divided into four groups for pre-incubation for 30 min at 37 °C: (1) no ATP and no PKCα, (2) 1 mM ATP and no PKCα, (3) no ATP and 0.05 μg PKCα/μg of RLIP76, and (4) 1 mM ATP and 0.05 μg PKCα/μg of RLIP76. Transport-assay was then carried out in the established manner by addition of proteoliposomes (RLIP76 or RLIP76 + p53, 250 ng each in 30 μL reaction mixture per filtration well, in triplicates) to transport buffer containing 3.6 μM 14C-DOX and either 0 or 4 mM ATP. ATP-dependent transport was calculated by subtracting uptake in the absence of ATP from that in the presence of 4 mM ATP. Results are average and standard deviation from three separate experiments, each in triplicates (n = 9).