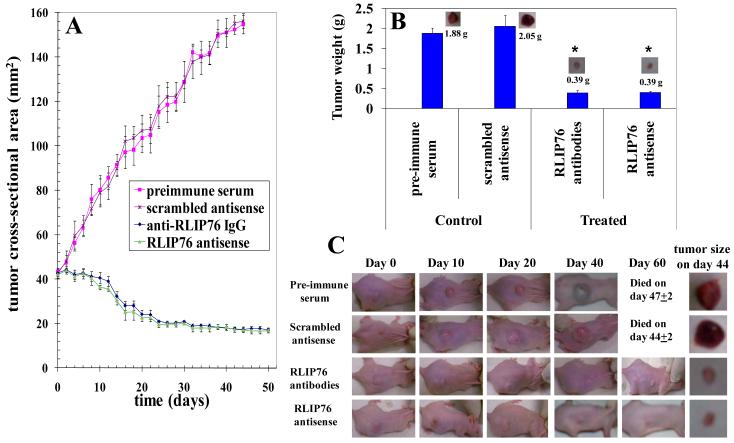
Figure 5.
Effect of anti-RLIP76 IgG and RLIP76-antisense on the size of subcutaneously implanted human Neuroblastoma cells in nude mice Twenty 11-weeks-old nu/nu mice were divided into four groups of 5 animals (treated with pre-immune serum, scrambled anti-sense DNA, anti-RLIP76 IgG, and RLIP76 antisense). All 20 animals were injected with 2 × 106 Neuroblastoma cells (SMS-KCNR) suspensions in 100 μl of PBS, subcutaneously into one flank of each nu/nu nude mouse. Animals were examined daily for signs of tumor growth. When tumors reached a cross-sectional area of ~ 40 mm2 (~30 days later), animals were randomized treatment groups as indicated in the figure. Treatment consisted of 200 μg of RLIP76-antibodies or antisense in 100 μl PBS, i.p. Control groups were treated with 200 μg/100 μl pre-immune serum or scrambled anti-sense DNA. Tumors were measured in two dimensions using calipers. Photographs of animals were taken at day 0, day 10, day 20, day 40 and day 60 after treatment are shown for all groups. Tumor-weights and photographs of tumors were also taken at day 44 after treatment. Tumor cross-sectional area in control and experimental groups (panels A and C); Tumor-weight at day 44 (panels B and C), *p < 0.001, n = 5.