Fig. 2. Flowchart describing overall methodology of significance assignment to a pathway.
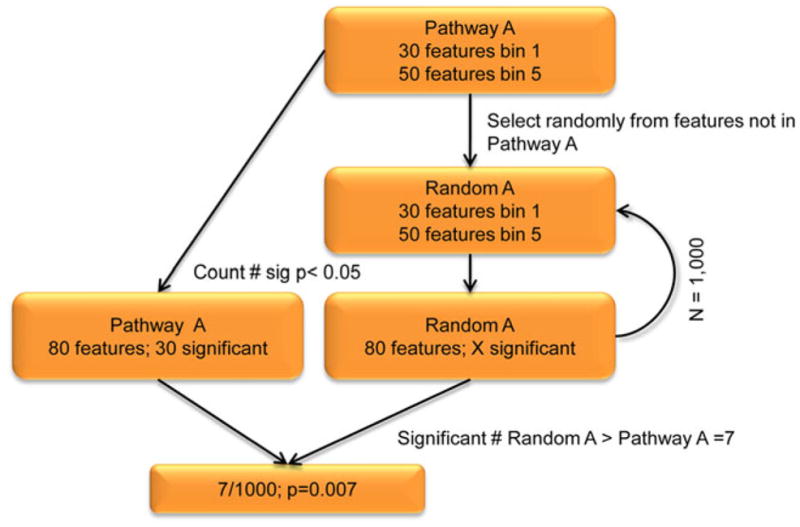
As an example, we analyze “Pathway A”, consisting of 80 total features (30 from bin 1 and 50 from bin 5). We consider a feature significant if any SNP found within has a p<0.05, and perform 1,000 permutation tests to assign significance to Pathway A. In our example Pathway A, we count 30 significant features. We randomly select from bins 1 (n=30 features) and 5 (n=50 features) to mimic the structure of Pathway A, creating “Random A”. Features are selected without replacement. We then count the number of significant features in Random A, replacing all features to their respective bins for the next iteration. We then create 999 more Random A pathways, tallying the number of times there are more significant features (p<0.05) in Random A than in Pathway A. This happens seven times in our hypothetical example giving us a p-value for Pathway A of 0.007.
