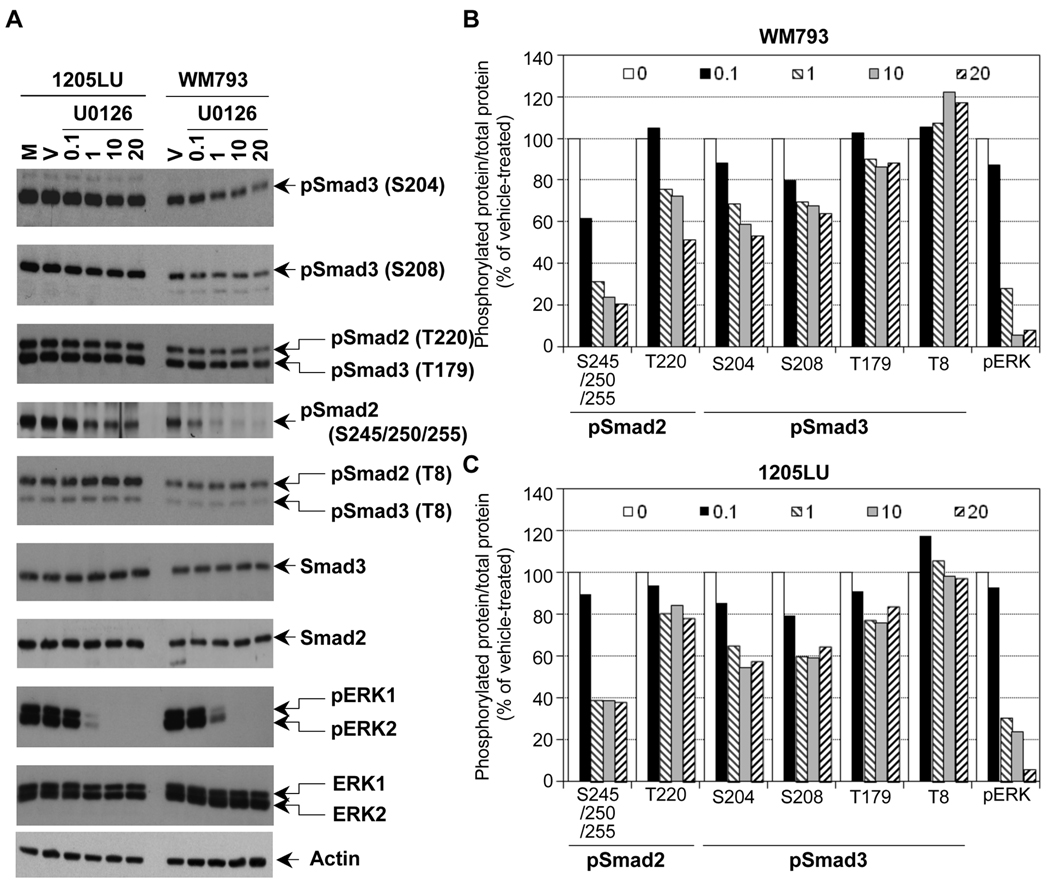
Figure 3. The linker phosphorylation of Smad2 and Smad3 in human melanoma lines involves ERK.
A. Partial inhibition of Smad2 and Smad3 linker phosphorylation in the presence of the MEK1/2 inhibitor, U0126. 24 hours post seeding, cells were serum-starved for about 16 hours, before the addition of the MEK1/2 inhibitor, U0126, at the indicated concentrations for 2 hours. Cells left two hours in serum-free medium (M) or treated with the vehicle DMSO (V) for two hours were used as controls. Whole cell extracts were then prepared. Immunoblots were performed with polyclonal antibodies against: Phosphorylated ERK1 (pERK1) and ERK2 (pERK2); total ERK1 and ERK2; Smad2 and Smad3 and the phosphorylated forms of Smad2 and Smad3, as in Figure 2. Densitometric analysis of the immunoblots in B and C. B. Ratio of phosphorylated protein/total protein for pSmad2, pSmad3 and pERK is represented as a function of U0126 concentration (0.1; 1; 10 and 20 µM as indicated in the legend; 0 is for vehicle) for the WM793 melanoma cell line. C. Ratio of phosphorylated protein/total protein for pSmad2, pSmad3 and pERK is represented as a function of U0126 concentration for the 1205LU melanoma cell line.