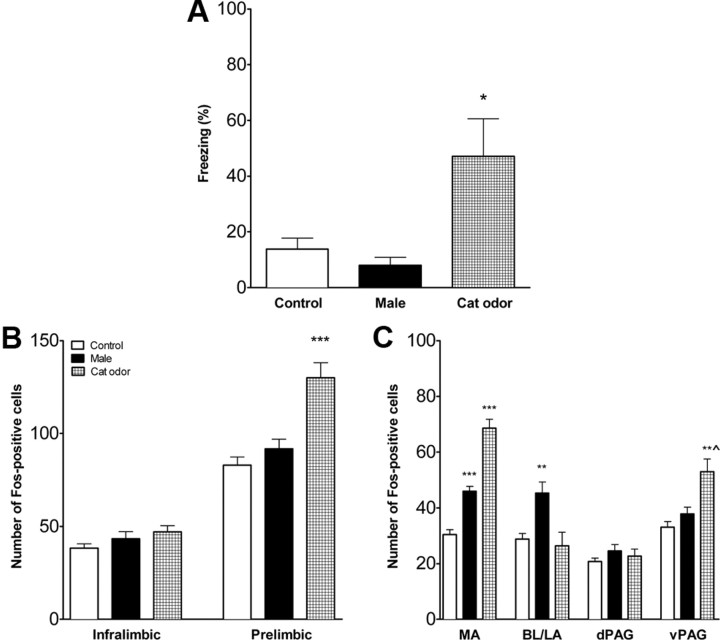
Figure 3.
Fear response and FOS expression in juvenile rats with intact mPFC. A, Percentage time freezing (mean ± SE) during exposure to an adult male rat or cat fur odor. Controls were exposed to an empty cage. Cat-odor-exposed rats froze significantly more than male-exposed or control rats. B, Activation of the mPFC in juvenile rats with intact mPFC. Number of FOS-positive cells (mean ± SE) was significantly increased in prelimbic mPFC of rats exposed to the threatening stimulus (cat odor). C, Activation of the amygdala and PAG in juvenile rats with intact mPFC. Exposure to the threatening stimulus (cat odor) increased the number of FOS-positive cells (mean ± SE) in the medial amygdala and ventrolateral PAG. Exposure to the nonthreatening stimulus (adult male) increased FOS in the medial and basolateral/lateral amygdala. MA, Medial amygdala; BL/LA, basolateral/lateral amygdala. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared with control; ∧p < 0.01 vs male exposure. n = 6–7 in each condition.