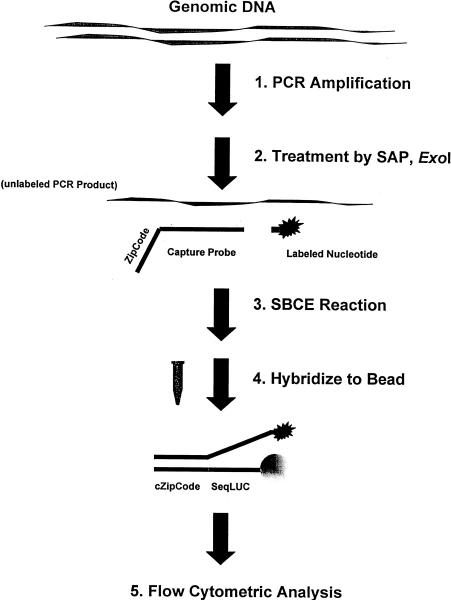
Figure 1.
Schematic presentation of the microsphere-based single base chain extension assays. DNA fragments containing the polymorphic site to be typed were amplified either individually or by multiplexed PCR (step 1). The PCR products containing a SNP site were pooled and treated with SAP and exonuclease I (step 2). After heat inactivation of the enzymes, the PCR products were used in the SBCE reactions (step 3) as described in Methods. For every SNP, one capture oligonucleotide probe with a unique ZipCode sequence was designed and used to assay the two alleles in each of two separate wells with a different labeled ddNTP per well. Multiplexed SNP analysis could be achieved by the employment of different ZipCode sequences for different SNPs in the presence of pooled PCR products. After the completion of the SBCE reaction, ∼1200 of each type of microsphere [with an attached oligonucleotide encoding the complement to the ZipCode sequences and a common luciferase sequence (SeqLUC)] were added to the completed SBCE reactions. The hybridization reactions were carried out at 40°C in the presence of NaCl for >2 hr (step 4). The microspheres were then subjected to flow cytometric analysis (step 5). Minimums of 100 of each type of microsphere were read and the mean value of MESF was used for determining the genotypes. The fluorescence signal of the corresponding microsphere without SBCE reactions (microsphere alone) or SBCE reactions without AmpliTaq FS were subtracted from the MESF values.