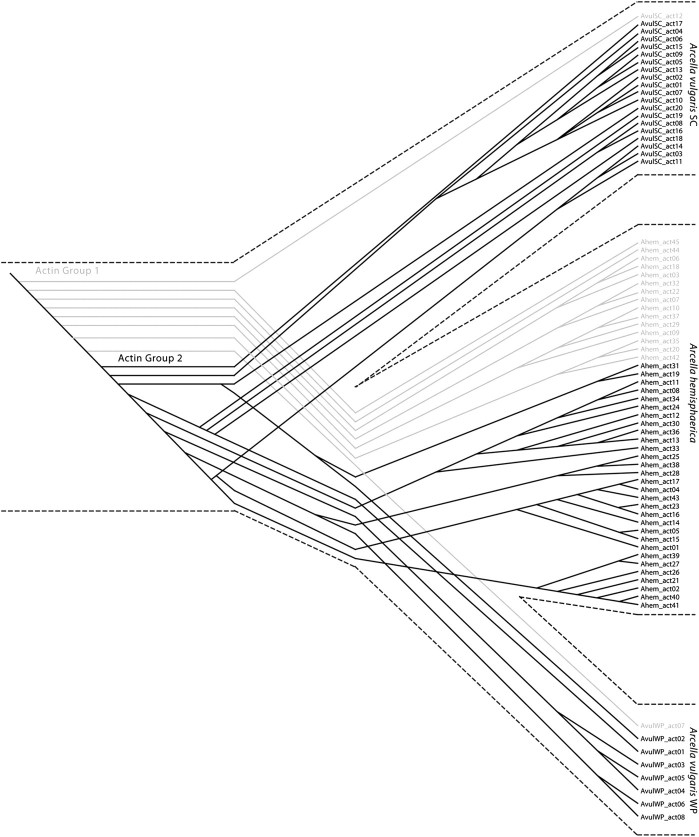
FIG. 7.
A hypothetical model for actin gene family evolution among species in the genus Arcella. The branching order for species is obtained from the SSU-rDNA reconstruction, and the branching order for actin paralogs is exactly as in figure 4. The first event depicted is the separation of actins in two genomic groups (Grey and Black), which predates the divergence of lineages. Following separation, each group is under distinct regulatory constraints. Perhaps, actins located in different areas are activated/deactivated following the life cycle, thus may be subject to different evolutionary pressures. Furthermore, speciation happens, with maintenance of the two actin groups in all three lineages. Within each lineage, there is a high level of independent duplications, the mechanism for which might be either a recombinational hotspot or a DRGR.