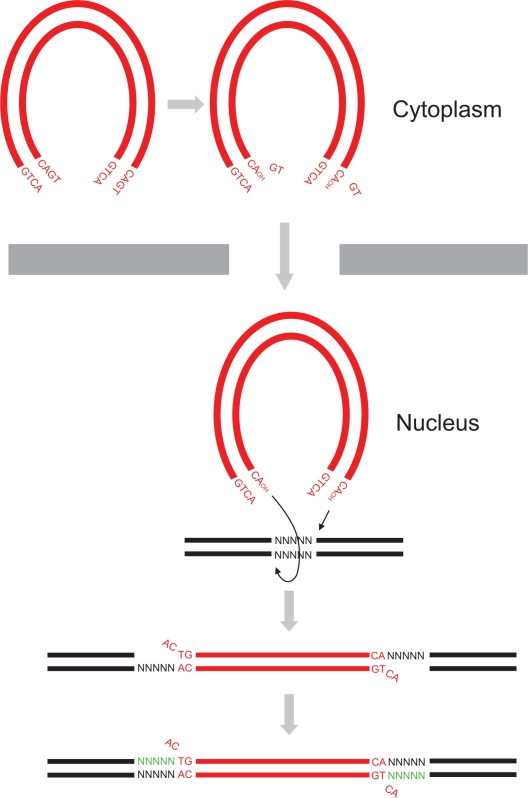
Figure 1.
HIV-1 DNA integration. HIV-1 virus synthesizes a dsDNA (red) copy of its RNA genome following entry of the virus into host cell cytoplasm. HIV-1 integrase removes 3′ end GT dinucleotides on both viral DNA ends to expose a 3′ hydroxyl group on terminal adenosines by 3′ processing. The 3′ processed viral DNA is then imported into the nucleus where strand transfer occurs resulting in the integration of the two viral DNA ends into host DNA (black) at positions five base pairs (bp) apart. Host DNA repair enzymes then cleave unpaired viral CA dinucleotides, fill in the five bp gaps (green), and ligate the DNA ends.