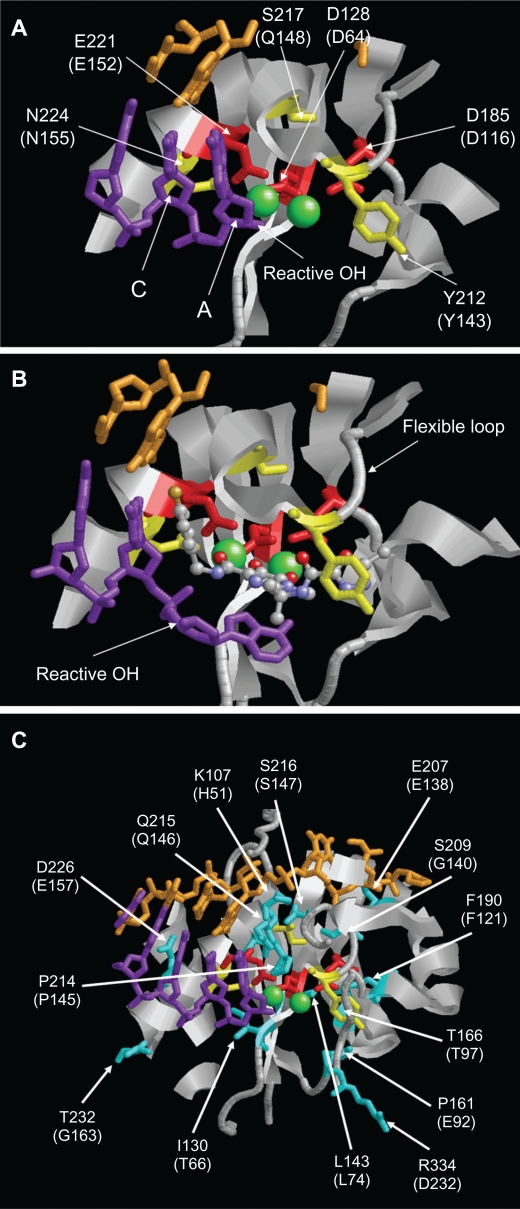
Figure 3.
Structure of the PFV IN active site. A) Structure of PFV IN active site within 14Å of Mn2+ ions showing location of the three active site residues (red sticks), three residues where primary resistance mutations occur (yellow sticks), and Mn2+ ions (green spheres). B) Structure of PFV IN active site in complex with raltegravir showing the three oxygen atoms (red spheres) of the β-hydroxy ketone moiety chelating the Mn2+ ions. The halobenzyl moiety (with brown fluoride atom) is seen stacked close to the cytosine (C) of the CA dinucleotide of the donor DNA strand (purple sticks) which results in the displacement of the terminal adenosine (A) and its 3′ hydroxyl group from the active site. C) Structure of PFV IN active site within 20Å of Mn2+ ions showing location of some of the residues where secondary resistance mutations occur (cyan sticks). PFV residues are indicated, and the corresponding HIV-1 residues are in brackets. The nontransferred DNA strand is shown as brown sticks. Protein data bank codes are 3OY9 and 3L2V,31 and the diagrams were created using RasMol software (University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA, USA).