Fig. 4.
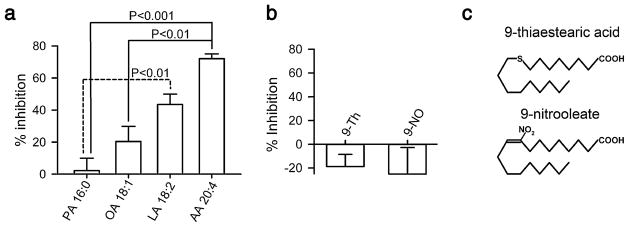
Inhibition of Cx46 hemichannel currents by other unsaturated fatty acids. a Dependence of the inhibitory effect on the number of unsaturated bonds. The effects of exposure to palmitic acid (PA, n=5), oleic acid (OA, n=5), linoleic acid (LA, n=6), or arachidonic acid (AA, n=6) for 5 min at 100 μM were determined. Protocol as described for Fig. 1d. Data are presented as means ± SEM. The labeling of the bars shows, for each fatty acid, the number of carbons followed by the number of double bonds; e.g., AA 20:4 for arachidonic acid, with 20 carbons and four double bonds. b Importance of the double bond at position 9. The experimental protocol was identical to that in a, but the fatty acids used were 9-thiastearic acid (9-Th) and 9-nitrooleate (9-NO). No statistically significant effects on the Cx46 hemichannel current were detected (n=7 for each compound). c Chemical structures of 9-thiastearic acid and 9-nitrooleate