Fig. 1.
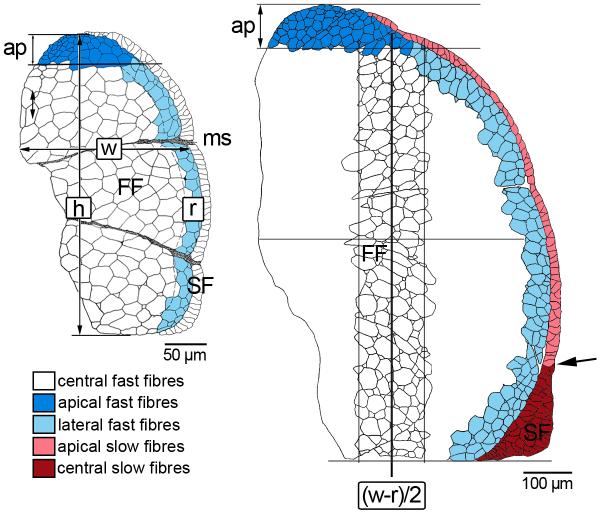
Zonal subdivision of fast and slow muscle for fibre size measurement as exemplified for epaxial quadrants of pearlfish at onset of exogeneous feeding (left) and at 82 dph (right): w width (maximum medio-lateral extension of fast muscle), h height (maximum dorso-ventral extension); boundary of lateral fast muscle growth zone delineated at r = 1/10 w; separating line of apical growth zone at ap = 1/10 h. From 82 dph onward, examination of the central fast fibre zone was confined to a representative transect centred at (w-r)/2, width defined as (w-r)/4, height as h-ap. Also beginning at 82 dph, the slow muscle domain was subdivided into monolayered apical zones and a multilayered central zone at the horizontal septum (demarcation indicated by arrow). FF fast fibres, ms myoseptum, SF slow fibres.