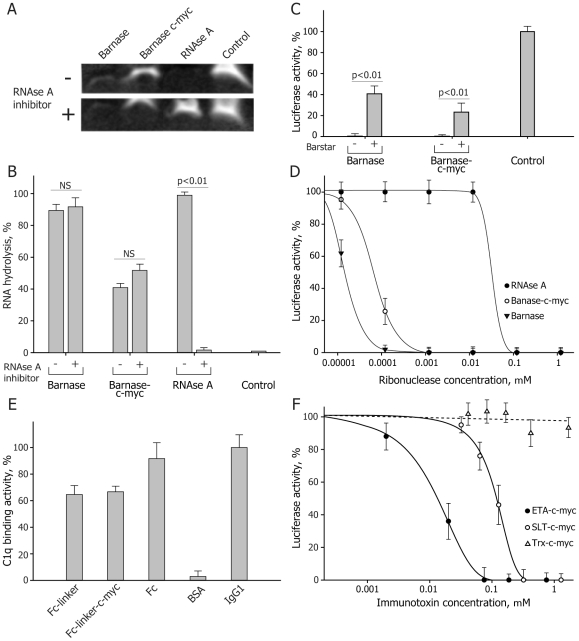
Figure 2. Functional in vitro activity of obtained IT.
(A) Representative hydrolysis of yeast RNA by recombinant barnase, barnase-c-myc and RNAse A in the absence or presence of RNAse inhibitor. (B) Quantitative analysis demonstrates that presence of pancreatic inhibitor of RNAse A does not affect the activity of barnase and barnase-c-myc. (C) Suppression of luciferase RNA translation in S30 ascites cell extract by barnase and barnase-c-myc in the presence or absence of barstar. (D) Barnase and barnase-c-myc are still inhibit luciferase RNA translation in concentrations of three orders of magnitude less than those for RNAse A. (E) Binding of the C1q component of the complement system to the Fc and Fc-c-myc molecules. Full-size Abs and their Fc fragments were used as a positive control. Recombinant Fc and Fc-c-myc molecules demonstrate the same affinity compared with native immunoglobulins. (F) Suppression of luciferase RNA translation in S30 ascites cell extract by Pseudomonas and SLT toxins. Activity of the RIPs was determined by decreasing of the level of luciferase mRNA translation in mouse Krebs-2 ascites cells S30 extracts depending on the IT concentration. Total inhibition of protein synthesis was detected at the ETA-c-myc concentration of 75 nM which was five times lower than for the SLT-c-myc molecule (320 nM). Bars in all experiments represent standard deviation (n = 3).