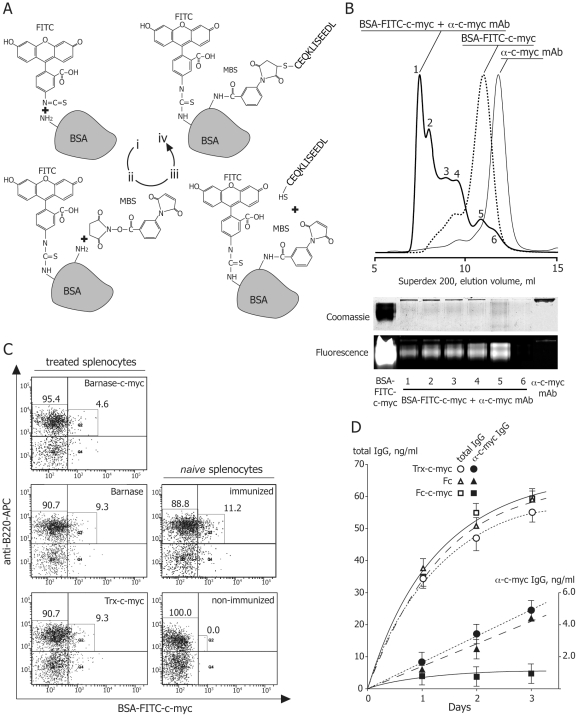
Figure 4. Barnase-c-myc and Fc-c-myc specifically deplete anti-c-myc B cells and decrease production of anti-c-myc Ab in culture of splenocytes, isolated from mice immunized by KLH-c-myc.
(A) Procedure of obtaining of BSA-c-myc conjugate labeled by FITC for flow cytometry detection of targeted anti-c-myc B cells. (i) Conjugation of BSA with FITC using coupling of isothiocyanate with primary amino groups. (ii) Reaction of free primary amino groups of BSA-FITC with MBS. (iii) Coupling of second functional group of MBS with SH group of N-terminal cysteine, flanking c-myc peptide. (iv) Final bifunctional reagent BSA-FITC-c-myc, which is capable to react with BCR on the surface of B cells due to the attached c-myc peptide and carrying fluorescein group for detection. (B) Binding of anti-c-myc mAb to BSA-FITC-c-myc in solution. Superdex 200 gel-filtration profile of BSA-FITC-c-myc alone (dashed line) and preincubated with anti-c-myc mAb (solid line). Anti-c-myc mAb are shown by thin solid line. Fractions from gel-filtration chromatography of BSA-FITC-c-myc preincubated with anti-c-myc mAb were subjected on PAGE and visualized by coomassie staining and measurement of FITC fluorescence emission (bottom panel). (C) Representative flow cytometry analysis of native splenocytes, isolated from non-immunized and immunized by KLH-c-myc mice, using BSA-FITC-c-myc and anti-B220 APC-labeled antibody (right panels). Approximately 11% of all B cells carry BCR specific for c-myc peptide (B220high BSA-FITC-c-mychigh, Q3 quadrant). Representative flow cytometry analysis of splenocytes, isolated from mice immunized by KLH-c-myc, treated by barnase-c-myc, barnase and Trx-c-myc (left panels from top to bottom). (D) Analysis of total antibody titer (open figures) and anti-c-myc Abs (filled figures) in samples of splenocytes, isolated from KLH-c-myc immunized mice, treated by Trx-c-myc (circles), Fc (triangles) and Fc-c-myc (squares) molecules. Bars represent standard deviation (n = 3).