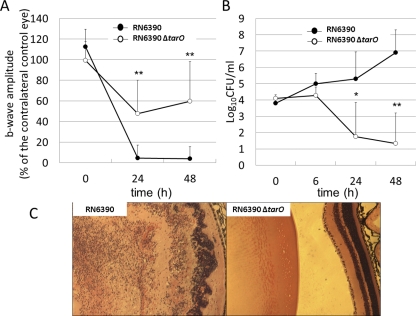
Figure 6.
Role of WTA in a mouse endophthalmitis model. (A) ERG. Retinal responsiveness of eyes infected with RN6390 (●) or RN6390ΔtarO (○). RN6390ΔtarO is significantly less able to establish endophthalmitis and cause vision loss. Data represent the mean ± SEM (n = 8). **P < 0.001 (in comparison to eyes infected with RN6390). (B) Number of viable RN6390 (●) or RN6390ΔtarO (○) recovered from mouse eyes. The numbers of recovered RN6390ΔtarO reduced significantly from 24 to 48 hours after inoculation. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 4–8). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001 (in comparison to the number of RN6390ΔtarO at 0 hours). (C) Histologic analysis. At 48 hours, eyes infected with RN6390 showed disruption of the retinal layers (left). In contrast, the retinas of eyes infected with RN6390ΔtarO had a normal appearance (right). Hematoxylin and eosin; magnification, ×4.