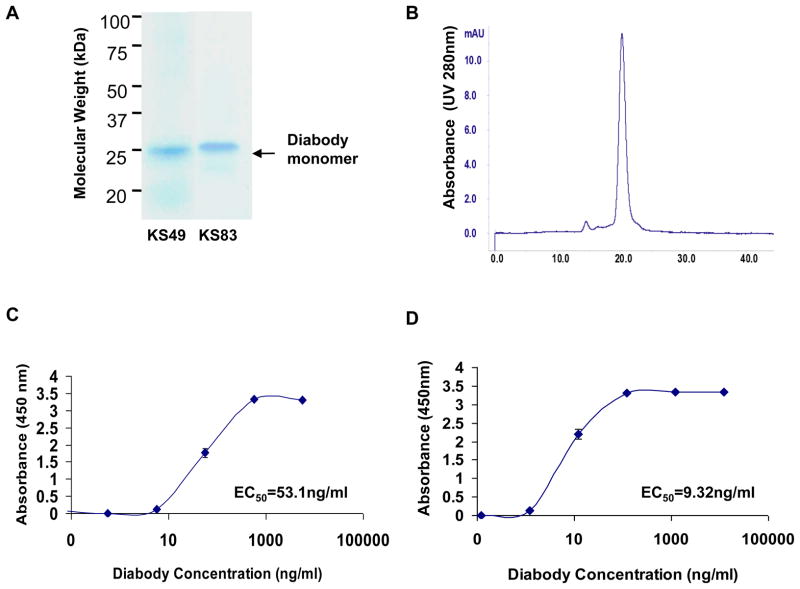
Figure 1. Biochemical characterization of constructed diabodies.
(A) SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining analysis of purified diabodies. Lane 1: KS49; Lane 2: KS83. Arrow indicates an appropriate molecular weight of diabody monomer. (B) Size-exclusion FPLC of purified diabody on a Superdex 75 column. Retention time of each sample was compared with appropriate molecular weight standards. (C) ELISA dose-response assay of KS49 diabody. Plates were coated with hEMP2 peptides, and 10-fold delusions (1:10-1:1×105) of the diabody preparations were assayed for binding. (D) ELISA dose-response assay of KS83 diabody. Plates were coated with mEMP2 peptides, and 10-fold delusions (1:10 to 1:1 × 106) of the diabody preparations were assayed for binding. For (C) and (D), EC50 was calculated. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments.