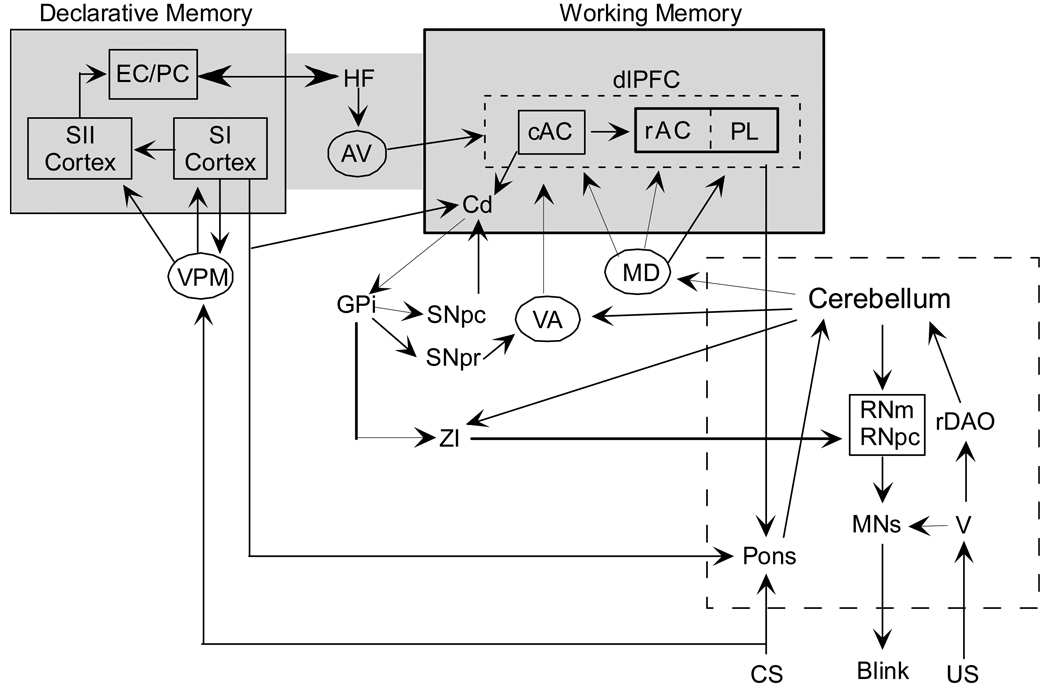
Figure 1.
A circuit diagram showing connections between the forebrain and cerebellum for whisker-signaled trace eyeblink conditioning. For tone-signalled conditioning the medial geniculate nucleus and auditory cortex would replace the VPM and somatosensory cortex. The pontine nuclei are indicated as the critical node between the forebrain and the cerebellum, and the thalamic nuclei are shown as the interface between the cerebellum and the different cortical regions. We have also hypothesized which parts of the circuit are more related to declarative memory and which parts are more related to working memory. The hippocampus is shown at an intersection of the two processes. The circuitry for these two processes are not yet confirmed, and may overlap. SI and SII: primary and secondary somatosensory cortex; VPM: ventral posterior medial thalamus; cAC: caudal anterior cingulate; rAC: rostral anterior cingulate; PL: prelimbic cortex; dlPFC: dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; AV: anteroventral thalamus; VA: ventral anterior thalamus; MD: dorsomedial thalamus; HF: hippocampal formation; BG: basal ganglia; RNm: magnocellular red nucleus; rDAO: rostral dorsal accessory olive; MNs: motor neurons; V: trigeminal nucleus; EC/PC: entorhinal / perirhinal cortex; ZI zona incerta; RNpc parvicellular red nucleus..