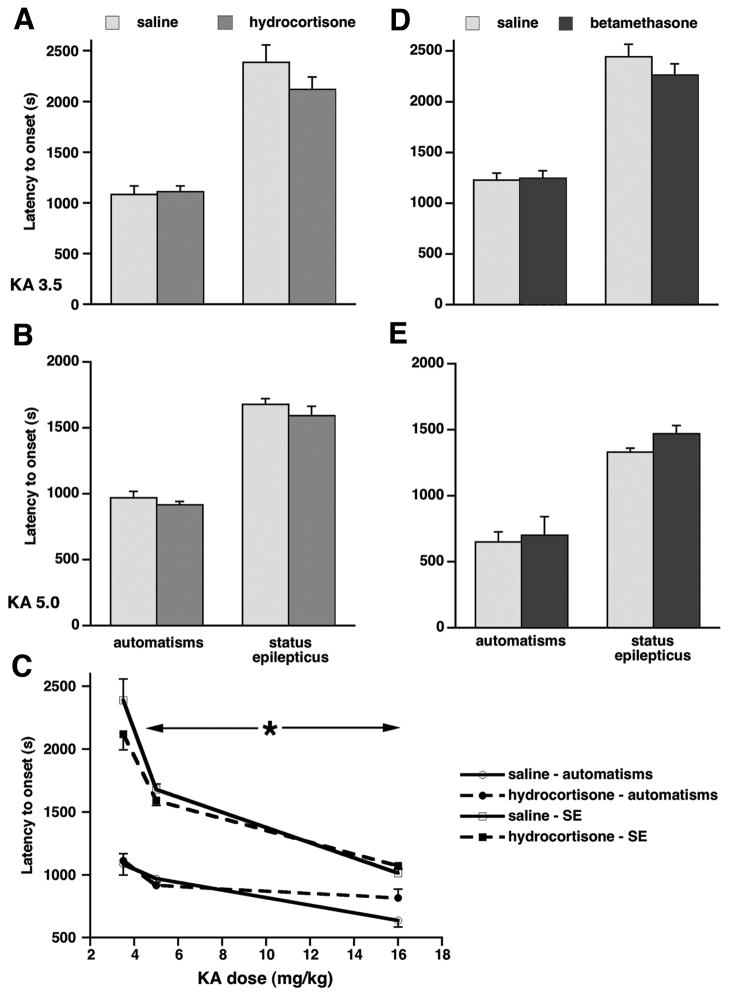
Figure 3. Prenatal exposure to either betamethasone or hydrocortisone does not alter susceptibility to kainic acid-induced seizures.
(A, B) There were no effects of prenatal hydrocortisone exposure on automatisms and status epilepticus induced by 3.5 mg/kg (C) or 5.0 mg/kg (D) of kainic acid.
(C) Overview of the KA dose-response for automatisms and status epilepticus in prenatally hydrocortisone- and saline-exposed rats. In addition to the 3.5 and 5.0 mg/kg doses, the dose of 16.0 mg/kg of KA was used. Two-way ANOVA revealed the effects of the KA dose for both symptoms (<-*-> p<0.05; significant difference only in the horizontal direction indicated by the arrows across the KA doses), but not of the prenatal exposure (vertical direction).
(D, E) Prenatal exposure to betamethasone did not change latency to onset of automatisms or status epilepticus induced by 3.5 mg/kg (A) or 5.0 mg/kg (B) of kainic acid compared to controls.