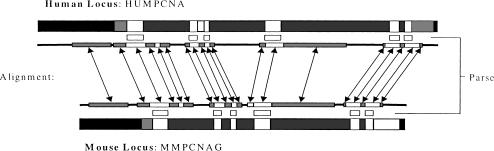
Figure 1.
Regions of the human and mouse homologous genes: Coding exons (white), noncoding exons (gray}, introns (dark gray), and intergenic regions (black). Corresponding strong (white) and weak (gray) alignment regions of GLASS are shown connected with arrows. Dark lines connecting the alignment regions denote very weak or no alignment. The predicted coding regions of ROSETTA in human, and the corresponding regins in mouse, are shown (white) between the genes and the alignment regions.