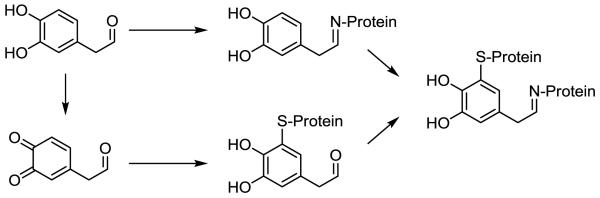
Figure 2.
Reactivity of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (DOPAL) involves modification of protein amines via the aldehyde. However, catechol oxidation is possible, yielding a thiol-reactive quinone, and such oxidation may explain the protein cross-linking observed for DOPAL. The spontaneous reaction of the DOPAL aldehyde with a protein primary amine (e.g., Lys) may yield a Schiff base as shown or an enamine product. Auto-oxidation of the DOPAL catechol, which is known to occur for DA, or enzyme-mediated oxidation (e.g., tyrosinase, prostaglandin-H-synthase) is predicted to result in formation of an ortho-quinone, which are known to be highly reactive for protein thiols (e.g., Cys).