Figure 1. 3C-based methods.
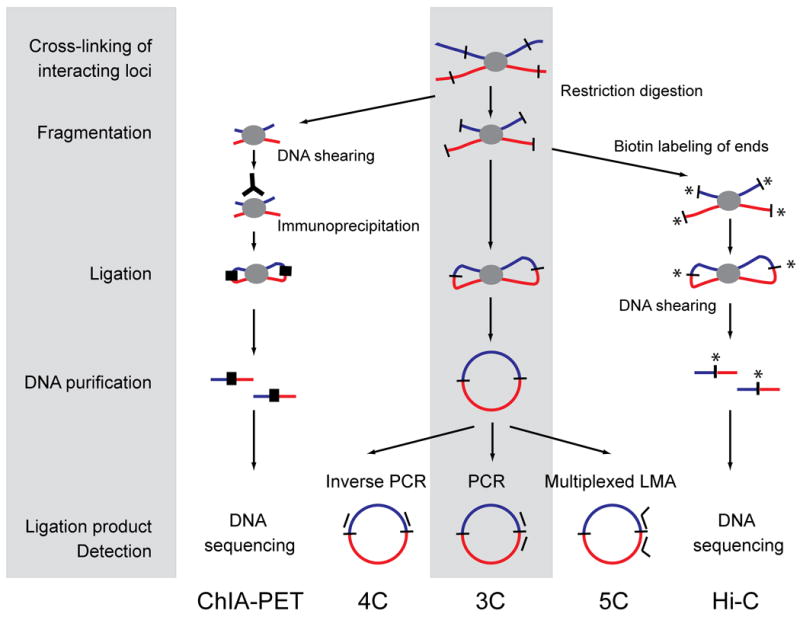
All 3C-based methods use the same principle of chromatin interaction detection (indicated in grey): cross-linking of interacting loci with formaldehyde, followed by DNA fragmentation, DNA ligation, DNA purification and finally ligation product detection. 3C employs restriction enzymes to fragment DNA, and regular PCR to detect ligation products, while 4C employs inverse PCR to detect all fragments ligated to a locus of choice. 5C uses multiplexed ligation mediated amplification (LMA) to detect large numbers of interactions simultaneously using pools of primers for thousands of loci of interest. CHiA-PET employs sonication to fragment cross-linked chromatin followed by an immunoprecipitation step prior to DNA ligation to enrich for loci bound by a protein of interest. Linkers are then ligated (black thick lines) and DNA is analyzed by direct deep sequencing. Finally, Hi-C employs restriction enzymes to fragment chromatin followed by filling in of the staggered ends using biotinylated nucleotides prior to DNA ligation. DNA is sheared and DNA fragments containing ligation junctions are purified using streptavidin-coated beads. DNA is then directly deep sequenced.
