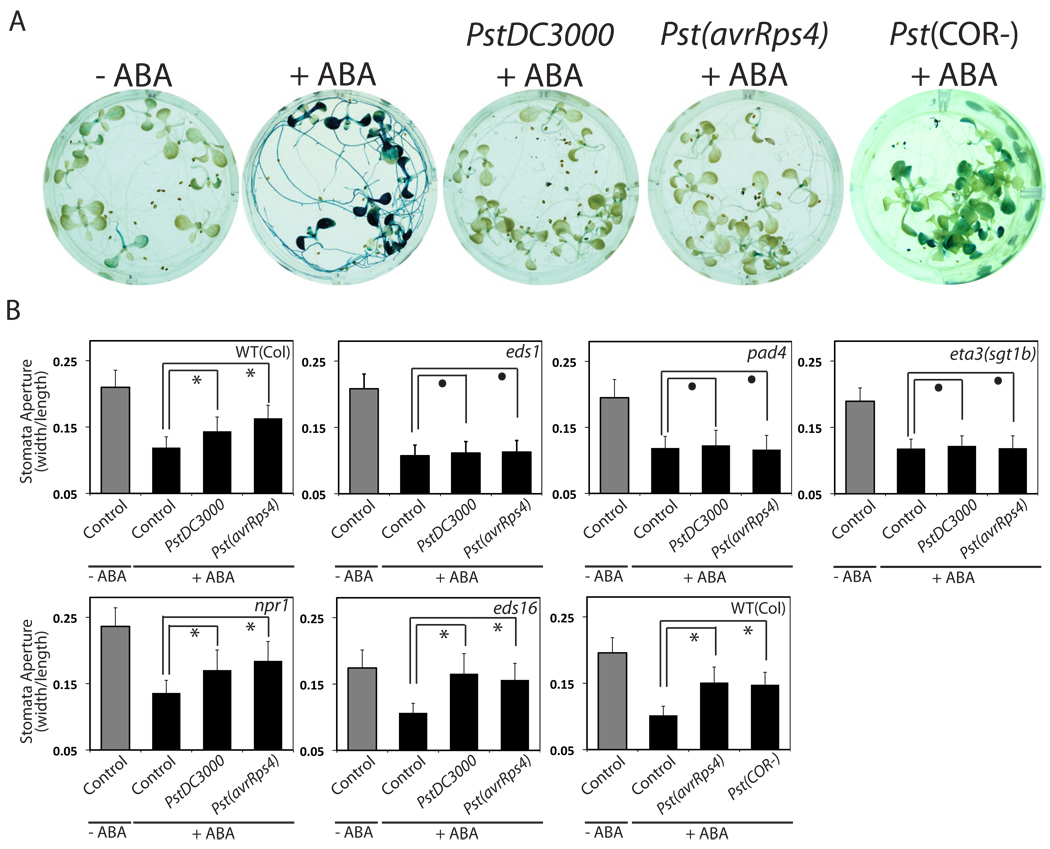
Figure 3. P. syringae infection inhibits ABA signaling through the EDS1/PAD4 pathway.
(A) Infections by Pseudomonas syringae pv tomato (Pst) DC3000, Pst(avrRps4) and Pst(COR-) inhibit ABA-induced RD29B reporter gene expression. (B) ABA-induced stomatal closing is inhibited by PstDC3000 and Pst(avrRps4) infection in an EDS1/PAD4/SGT1b-dependent manner but independently of NPR1 and EDS16. Infections by Pst(COR-) also inhibit ABA-induced stomatal closing. Symbols * and • represent p< 0.025 and p> 0.2, respectively (n=3 experiments, 30 stomata per experiment and condition, 2-tail T-test). Error bars mean ± s.e.m. (n=3). ABA was applied at 10 µM (A–B).