Figure 2.
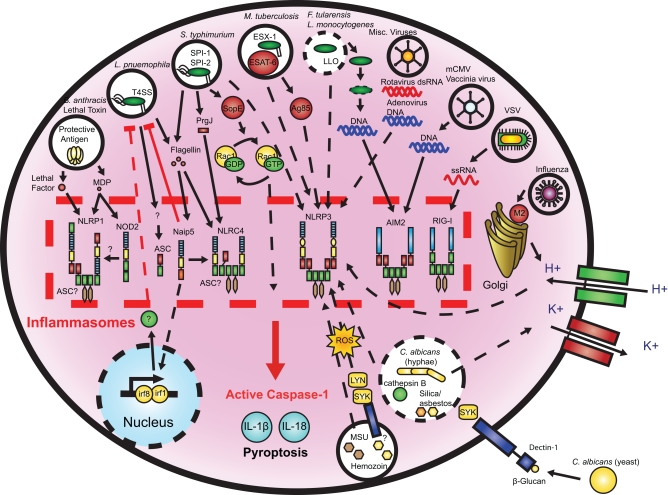
Microbial activation of the inflammasomes. Pathogenic microorganisms activate the inflammasomes through multiple agonists and pathways. S. typhimurium, L. pneumophila, and M. tuberculosis reside within the host cell phagosome and are capable of activating inflammasomes through secreted flagellin, effectors, or undefined NLRP3 agonists. F. tularensis and L. monocytogenes, which escape the phagosome activate AIM2 that senses cytosolic DNA. B. anthracis lethal toxin activates the NLRP1 inflammasome. C. albicans and hemozoin activate NLRP3 through SYK signaling. Viral-mediated inflammasome activation is heavily dependent on the detection of nucleic acids by NLRP3, AIM2, and RIG-I. Dotted lines indicate signaling through an unknown mechanism.