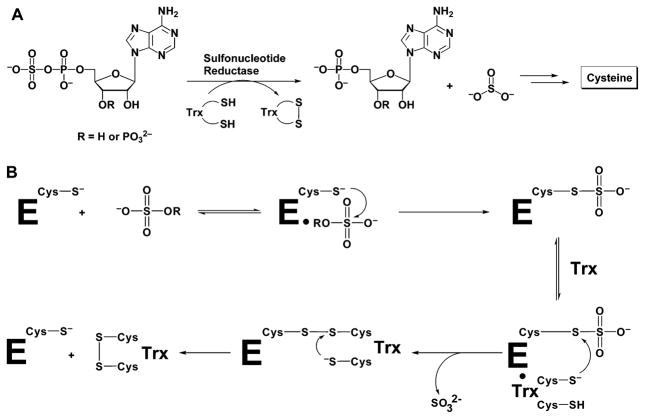
Figure 1.
(A) Depending on the organism, APS or PAPS is reduced to sulfite by APS reductase or PAPS reductase, respectively. The sulfite product formed in this reaction is further reduced to sulfide, and the sulfur is incorporated into cysteine. This amino acid is then converted into numerous metabolites, including methionine and cofactors, such as coenzyme A. (B) Mechanism proposed for sulfonucleotide reduction.