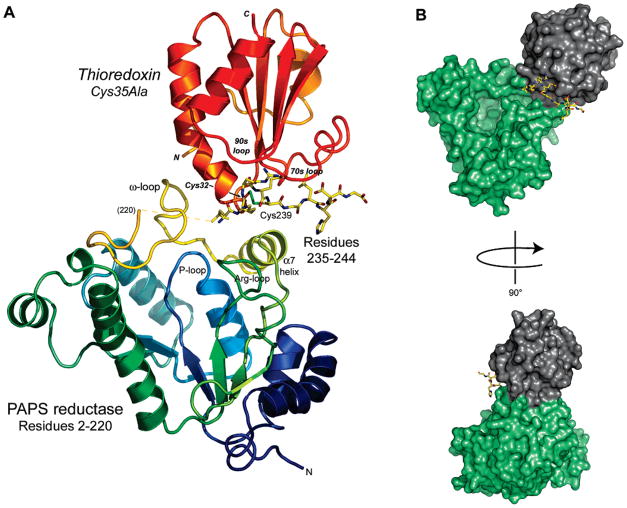
Figure 3.
Overall view of the PAPS reductase–Trx1 complex in the cocrystal structure. (A) The flexible C-terminal tail of the reductase (residues 235–244; all atoms shown) fits into a groove on Trx1 comprised of the 30s, 70s, and 90s loops (Trx1 residues 28–33, 71–77, 91–96, respectively; Trx1 residues in italics); the mixed disulfide is formed between Cys239 of the reductase and Cys32 of Trx. Trx in turn is bound to PAPS reductase among an ω-loop (residues 202–212, colored yellow), helix α7, and the C-terminal Cys239-peptide (residues 235–244). Residues 221–234 of PAPS reductase are disordered in the cocrystal structure (indicated by a dashed yellow line in front of the ω-loop). (B) Solvent accessible surface depiction of the PAPS reductase–Trx1 complex. In panel B and in Figures 4 and 5, PAPS reductase residues 1–220 are colored green, C-terminal peptide residues 235–244 are colored yellow, and Trx is colored gray.