Table 1. Potency of a Series of (N)-Methanocarba Adenosine Derivatives at Three Subtypes of Human ARs and the Functional Efficacy at the A3AR.
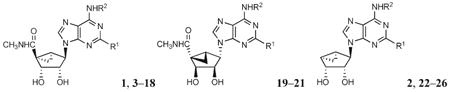 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| compd | structure | affinity (Ki, nM) or % inhibitiona | % efficacy,b A3 | |||
| R1 | R2 | A1 | A2A | A3 | ||
| Series A | ||||||
| 1ac | Cl | 3-Cl-Bn | 260 ± 60h | 2300 ±100 | 0.29 ± 0.04 | 103 ± 7 |
| 1b | Cl | 3-I-Bn | 136 ± 22d,h | 784 ± 97d | 1.5 ± 0.2c | 100c |
| 3c | H | 3-I-Bn | 700 ± 270h | 6200 ± 100 | 2.4 ± 0.5 | 100 |
| 4c | Cl | cyclopentyl | 18.3 ± 6.3h | 3250 ± 300 | 3.7 ± 0.9 | 101 |
| 5 | C≡C(CH2)2COOH | 3-Cl-Bn | (17 ± 4%) | (24 ± 12%) | 61.1 ± 35.8 | 106 ±18 |
| 6c,e | C≡C(CH2)3COOH | 3-Cl-Bn | 14,900 ± 3500h | (43%) | 2.38 ± 0.56 | ND |
| 7 | C≡C(CH2)4COOH | 3-Cl-Bn | (11 ± 5%) | (38 ± 2%) | 12.4 ± 1.8 | 74.4 ± 5.1 |
| 8 | C≡C(CH2)2COOCH3 | 3-Cl-Bn | (41 ± 0%) | (43 ± 5%) | 5.5 ± 0.3 | 90.0 ± 6.2 |
| 9c | C≡C(CH2)3COOCH3 | 3-Cl-Bn | 482 ± 23h | (49%) | 1.17 ± 0.27 | ND |
| 10 | C≡C(CH2)4COOCH3 | 3-Cl-Bn | (20 ± 7%) | 3540 ± 1370 | 11.1 ± 2.3 | 85.0 ± 10.2 |
| 11 | C≡C(CH2)2CONH(CH2)2NH2 | 3-Cl-Bn | 2320 ± 520 | 550 ± 83 | 2.5 ± 0.5 | 96.9 ± 6.8 |
| 12c | C≡C(CH2)3CONH(CH2)2NH2 | 3-Cl-Bn | 454 ± 44h | (81%) | 2.17 ± 0.51 | ND |
| 13 | C≡C(CH2)4CONH(CH2)2NH2 | 3-Cl-Bn | (47 ± 3%) | 277 ± 33 | 3.4 ± 0.7 | 100 ± 2 |
| 14 | C≡C(CH2)2CONH(CH2)3NH2 | 3-Cl-Bn | (31 ± 9%) | 979 ± 181 | 3.1 ± 0.4 | 97.9 ± 18.4 |
| 15 | C≡C(CH2)2CONH(CH2)4NH2 | 3-Cl-Bn | (30 ± 2%) | 766 ± 109 | 2.1 ± 0.4 | 102 ± 13 |
| 16 | C≡C(CH2)2CO[NH(CH2)2]2NH2 | 3-Cl-Bn | (33 ± 2%) | 890 ± 110 | 15.4 ± 4.4 | 87.6 ± 21.2 |
| 17a | C≡C(CH2)2CONH(CH2)2NH-biotin | 3-Cl-Bn | (1 ± 1%) | (51 ± 2%) | 36.4 ± 5.6 | 84.5 ± 12.0 |
| 17b | C≡C(CH2)2CONH(CH2)2NH-CO(CH2)5NH-biotin | 3-Cl-Bn | (12 ± 4%) | (47 ± 11%) | 57.7 ± 16.2 | 107 ± 18 |
| 18 | C≡C(CH2)2CONH(CH2)2NH-CO-(CH2)5Cy5g | 3-Cl-Bn | (36 ± 3%) | 4730 ± 1020 | 17.2 ± 3.1 | 94.4 ± 9.6 |
| Series B | ||||||
| 19 | C≡C(CH2)3COOH | 3-Cl-Bn | (0%) | (9 ± 2%) | 5270 ± 1090 | ND |
| 20 | C≡C(CH2)2CONH(CH2)2NH2 | 3-Cl-Bn | (33 ± 7%)h | (8 ± 1%) | (30 ± 1%) | 25.6 ± 10.9 |
| 21 | C≡C(CH2)4CONH(CH2)2NH2 | 3-Cl-Bn | (36 ± 5%)h | (5 ± 1%) | 4630 ± 1060 | 52.0 ± 9.4 |
| Series C | ||||||
| 2ad | Cl | 3-Cl-Bn | 3070 ± 1500h | 4510 ± 910 | 1.06 ± 0.36 | 2.9 ± 3.7f |
| 2bd,e | Cl | 3-Br-Bn | 1760 ± 1010h | 1600 ± 480 | 0.73 ± 0.30 | 46 ± 4,5.8 ± 0.8f |
| 2cd,e | Cl | 3-I-Bn | 3040 ± 610h | 1080 ± 310 | 1.44 ± 0.60 | 44 ± 6, 1.0 ± 3.2f |
| 22 | H | 3-Cl-Bn | 1600 ± 150 | 4520 ± 830 | 4.9 ± 0.7 | 58.3 ± 8.0 |
| 23 | H | 3-I-Bn | 839 ± 68 | 2330 ± 680 | 11.0 ± 2.2 | 80.8 ± 19.0 |
| 24 | F | 3-I-Bn | 513 ± 4 | 4000 ± 780 | 10.7 ± 0.9 | 19.0 ± 3.0 |
| 25 | Cl | cyclopentyl | 109 ± 16 | 1640 ± 360 | 120 ± 31 | 95.1 ± 4.6 |
| 26 | C≡C(CH2)2CONH(CH2)2NH2 | 3-Cl-Bn | (15 ± 2%) | (35 ± 6%) | 404 ± 67 | 0.9 ± 8.5 |
All experiments were done on CHO or HEK293 (A2A only) cells stably expressing one of four subtypes of human ARs. The binding affinity for A1, A2A, and A3ARs was expressed as Ki values (n = 3–5) and was determined by using agonist radioligands ([3H]51, [3H]54, or [125I]53, respectively), unless otherwise noted. A percent in parentheses refers to inhibition of radioligand binding at 10 μM.
Unless otherwise noted, the efficacy at the human A3AR was determined by inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP production in AR-transfected CHO cells. At a concentration of 10 μM, in comparison to the maximal effect of 51 (= 100%) at 10 μM. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error (n = 3). ND, not determined.
Values from Melman et al.20
A3AR functional assay consisted of stimulation of [35S]GTPγS binding at 10 μM, expressed as a percentage of the full effect induced by 10 μM 51 (100 ± 5%).
Structure given in Scheme 1B.
A1AR binding determined using [3H]52.
