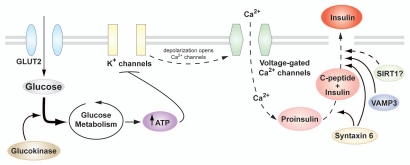
Figure 3.
Glucose metabolism and insulin secretion in the β-cell. Glucose enters the β-cell through the facilitative GLUT2 transporter and is metabolized during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, resulting in rapid generation of ATP and closure of the ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Subsequent plasma membrane depolarization leads to opening of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, and the consequent influx of Ca2+ triggers insulin granule exocytosis. Also shown are genes important for insulin granule maturation, transport and docking to the plasma membrane of the β-cell.