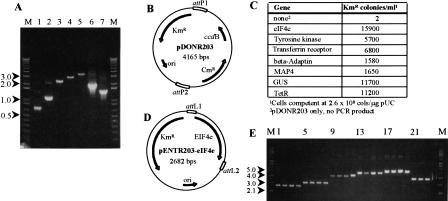
Figure 2.
(A) Agarose gel (1%) of PCR amplification products (2.5 μL of 35 μL) using attB-primers (see Methods) encoding eIF4e (lane 1), tyrosine kinase (lane 2), transferrin receptor (lane 3), β-adaptin (lane 4), MAP4 (lane 5), glucuronidase (Gus, lane 6), or the tetracycline-resistance gene (TetR; lane 7). (B) attP cloning vector pDONR203. PCR products cloned by in vitro recombination replace the chloramphenicol-resistance and ccdB genes; the recombination reactions convert the attP sites to attL sites. (C) Colonies resulting from transformation of E. coli with reactions (2 μL of 22 μL) containing the PCR products, pDONR203, and BP Clonase. The negative control contained all components except PCR product. (D) Entry Clone pENTR203-eIF4e, the product of recombinational cloning of the eIF4e PCR product into pDONR203. (E) Miniprep DNA (Entry Clones) from the colonies in C. Lanes 1–4, eIF4e; lanes 5–8, tyrosine kinase; lanes 9–12, transferrin receptor; lanes 13–16, β-adaptin; lanes 17–20, MAP4; lanes 21–24, Gus; M, supercoiled DNA ladder.