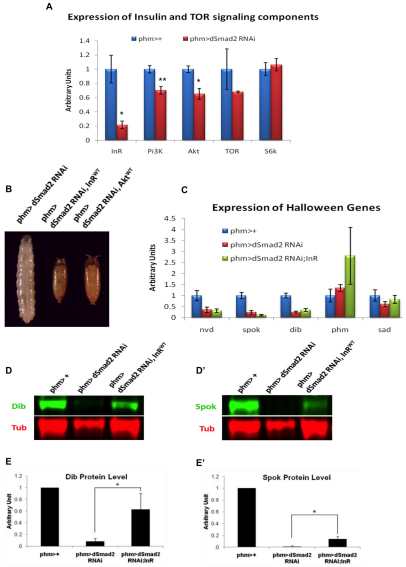
Fig. 5.
Loss of Activin signaling in the PG reduces insulin receptor expression and lowers Halloween gene protein levels. (A) The transcript levels of InR, Pi3K, Akt, TOR and S6k in the BPGC of the control and the dSmad2 RNAi larvae. Data are mean±s.d. (B) Expression of either a UAS-InR or a UAS-Akt transgene in the PG rescues the dSmad2 RNAi larvae to the adult stage. (C) Comparison of the transcript levels of the Halloween genes in the control, dSmad2 RNAi and phm>dSmad2 RNAi; InR larvae. No statistical differences are found between dSmad2 RNAi larvae and phm>dSmad2 RNAi; InR larvae. Data are mean±s.d. (D,D′) Western blot analysis on Dib and Spok proteins levels in the control, dSmad2 RNAi and phm>dSmad2 RNAi; InR larvae. (E,E′) Quantitation. The levels of Dib and Spok are normalized to Tubulin and are relative to the phm>+ animals. Data are mean±s.d. *P<0.05, **P<0.005.