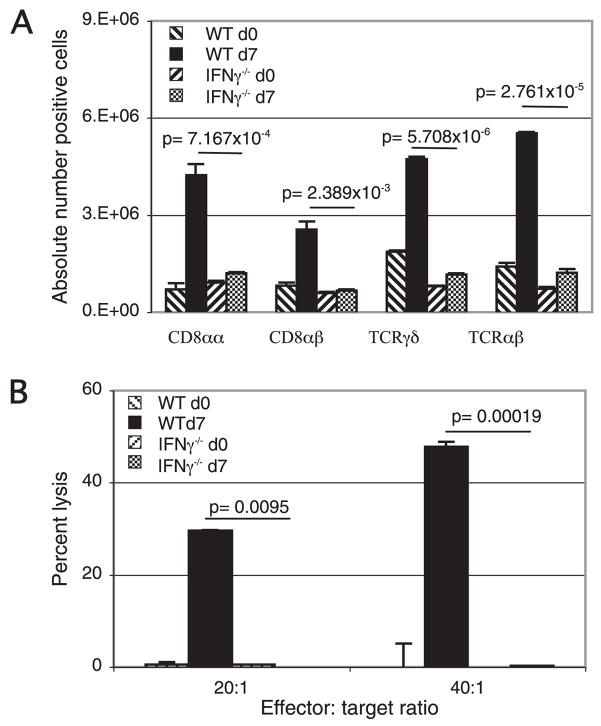
FIGURE 4.
IFN-γ−/− mice exhibit a suboptimal IEL response against E. cuniculi infection. IEL from IFN-γ−/− and WT mice (n = 6 mice/group) were isolated 7 days p.i. A, Induction of IEL response in IFN-γ−/− mice following oral E. cuniculi infection. IFN-γ−/− and WT mice orally infected with E. cuniculi were sacrificed at day 7 p.i., and IEL were purified (n = 4 mice/group). Isolated IEL were assayed for CD8αα, CD8αβ, TCRαβ, and TCRγδ expression by FACS analysis. Data represent the mean ± SD of two individual sets of experiments. B, Cytotoxic activity of IEL against E. cuniculi-infected macrophages. IEL from IFN-γ−/− and WT mice were incubated with 51Cr-labeled uninfected and infected macrophages at different E:T ratio (20:1, 40:1). After 4 h of incubation, the cytolytic activity was determined by radioisotope release into culture supernatant. The experiment was performed twice with similar results and data are representative of one experiment.