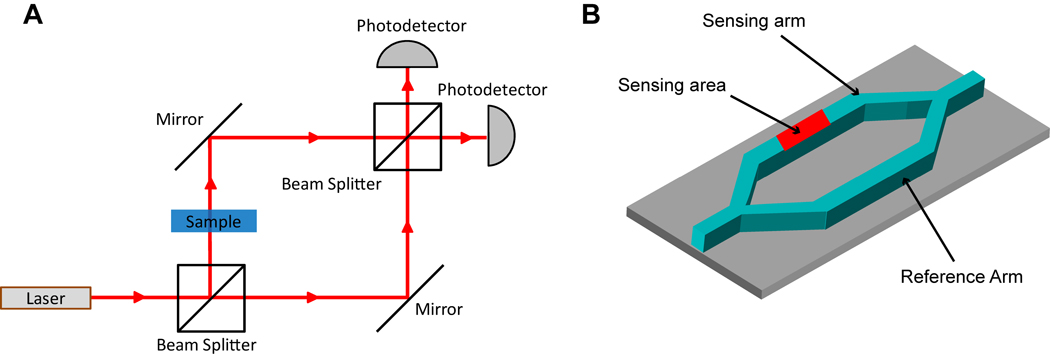
Fig. 3.
(A) A schematic of a classic free space Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Light from a light source is split into two paths (sample and reference) at a beam splitter and then recombined at another beam splitter whereupon the degree of interference is measured at a photodetector. The interference is due to a higher refractive index sample slowing down the light in the sample path. (B) Illustration of an on-chip Mach-Zehnder interferometer with a Y-junction splitting a waveguide into a sensing arm and a reference arm.