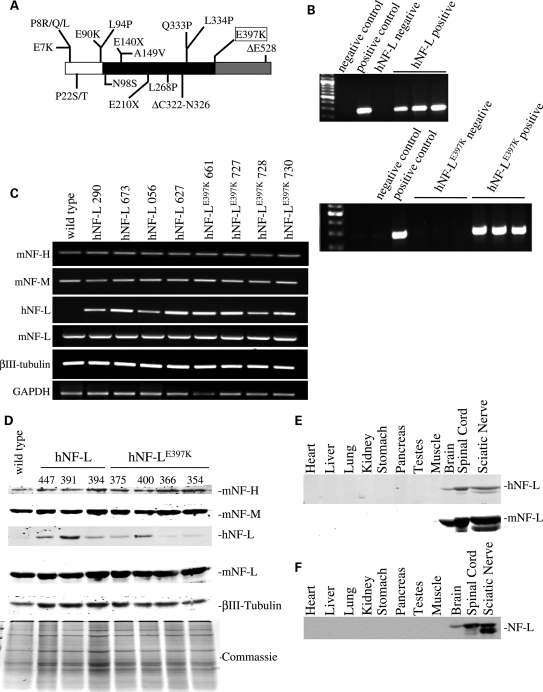
Figure 1.
Expression of hNF-LE397K in mice does not affect expression of other cytoskeletal elements. (A) Schematic of hNF-L protein with 18 reported mutations indicated. White indicates the N-terminal head domain, black indicates the coil-coiled rod domain and gray indicates the C-terminal tail domain. hNF-LE397K occurs at the end of the rod domain in the most conserved sequence in the intermediate filament family (KLLEGEE). (B) Transgenic lines were identified by PCR analysis of genomic DNA derived from tail biopsies. Four lines of hNF-L and hNF-LE397K mice were identified, three of which are shown here. hNF-L was not amplified from wild-type genomic DNA. The endogenous hNF-L promoter drove expression of wild-type and hNF-L. For both upper and lower panels: negative control was no genomic DNA; hNF-L and hNF-LE397K negative controls were wild-type C57Bl6 mice. (C and D) To determine the effect of expressing wild-type and mutant hNF-L on endogenous mouse cytoskeletal proteins, mRNA (C) and protein (D) levels were analyzed. (C) Expression of hNF-L, hNF-LE397K, mNF-L, NF-M, NF-H and βIII-tubulin was analyzed by reverse-transcription PCR amplification of mRNA purified from spinal cords of wild-type, hNF-L and hNF-LE397K mice. hNF-L transgenes did not alter transcription of other cytoskeletal components. (D) Sciatic nerve lysates were fractionated on 7.5% SDS–polyacrylamide gels from 6-month-old animals and immunoblotted with antibodies recognizing hNF-L (α-NF70kDa), mNF-L (DA2), NF-M (RMO44), NF-H (CPCA-NF-H) and neuron-specific βIII-tubulin (TUJI). Low levels of hNF-L and hNF-LE397K proteins were detected in transgenic mice. hNF-L transgenes did not affect expression of endogenous NF subunits or βIII-tubulin. (E and F) Utilizing the endogenous hNF-L promoter did not result in ectopic expression of hNF-L transgenes. Lysates from various tissues were fractionated on 7.5% SDS–polyacrylamide gels from 3–4 (E) and 14 (F) months old animals and immunoblotted with an antibody that recognizes both mouse and hNF-L (DA2). All analysis was performed on at least three hNF-L and hNF-LE397K mice.