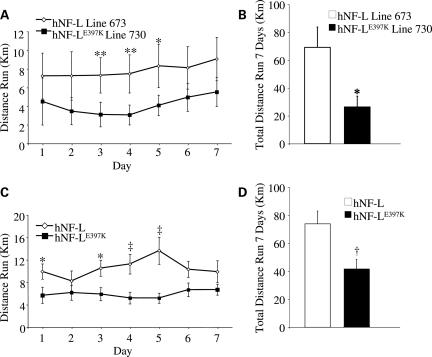
Figure 4.
hNF-LE397K mice have reduced voluntary activity. Mice of 1–4 months of age were given free access to running wheels for a period of 7 days. Revolutions were stored on activity wheel counters and then converted into kilometers on the basis of a 5 in. diameter running wheel. (A) Daily and (B) total activity were monitored in a single line of hNF-L and hNF-LE397K mice. Daily activity was significantly reduced at days 3–5 in line 730 hNF-LE397K relative to line 673 hNF-L. Total activity over 7 days was also significantly reduced. To determine whether reduced activity was unique to line 730, all lines of hNF-LE397K and hNF-L were monitored. (C) For all lines of mice, daily activity was significantly reduced relative to control at days 1, 3–5. (D) Additionally, total activity over 7 days was significantly reduced in all lines of hNF-LE397K mice. Means for each daily activity were analyzed for overall statistical differences by two-way repeated-measures ANOVA, followed by Holm–Sidak post hoc analysis. Means for total distance run were analyzed by unpaired t-test. *P< 0.05, **P< 0.02, †P< 0.008, ‡P< 0.005. For analysis of individual lines, at least six mice were analyzed per genotype. For all lines, at least 13 mice were analyzed for each genotype.