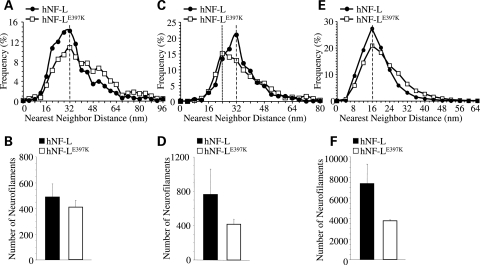
Figure 7.
NFs of proximal sensory and small motor axons are altered in mice expressing hNF-LE397K. Axoplasmic organization was analyzed in proximal sensory and motor axons from age-matched hNF-L controls and symptomatic hNF-LE397K mice. Distributions of NND for sensory (A) as well as small (C) and large (E) motor axons from both hNF-L and hNF-LE397K mice. Peak NND was unaffected in both sensory (A) and large motor (E) axons, whereas peak NND in small (C) motor axons was reduced in hNF-LE397K axons. In sensory axons, the number of NFs was reduced between 16 and 36 nm, whereas between 40 and 64 nm NF number was increased in hNF-LE397K axons (A). However, the total number of NFs in sensory nerves was not different between control and hNF-LE397K axons (B). For small motor axons, NF number was reduced within the range of 28–34 nm in hNF-LE397K axons (C), and large motor axons had fewer NFs between 8 and 16 nm, whereas they had more NFs between 28 and 40 nm in hNF-LE397K axons (E). Both small (D) and large (F) motor axons from hNF-LE397K axons had reduced numbers of total NFs. However, these differences were not statistically significant. Total NF numbers were analyzed for statistical significance by Student's t-test (sensory axons) and Welch's t-test (small and large motor axons). NND was analyzed in at least three mice per genotype in motor axons and four mice per genotype in sensory axons.