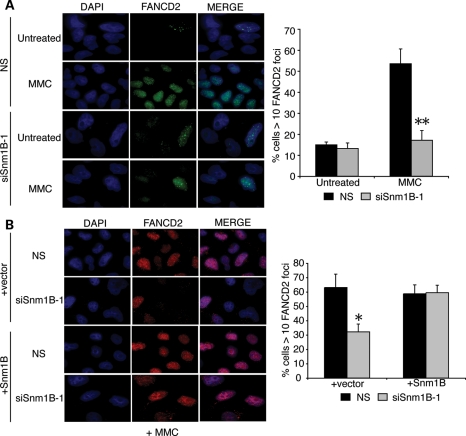
Figure 2.
MMC-induced FANCD2 foci formation is impaired in SNM1B-depleted cells. (A) FANCD2 foci formation in SNM1B-depleted cells. HeLa cells transfected with NS or siSNM1B-1 were treated with MMC (330 ng/ml) for 8 h at 48 h post-transfection. Cells were fixed with p-formaldehyde and stained using α-FANCD2 antibodies (green). Nuclei were stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). The percentage of cells with greater than 10 FANCD2 foci was determined. At least 300 nuclei were scored for each sample. All images were acquired at ×100 magnification. Representative images are shown. Graph represents average percentage of foci-positive cells from three independent experiments with standard deviation. **P< 0.005, Student's two-tailed t-test. (B) Expression of siRNA-resistant SNM1B complements the ICL-induced FANCD2 foci defect in SNM1B-depleted cells. HeLa cells expressing an siSNM1B-1-resistant SNM1B cDNA were transfected with NS or siSNM1B-1. Transfected cells were treated with MMC (330 ng/ml) for 8 h. Cells were fixed with p-formaldehyde and stained using α-FANCD2 antibodies (red). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). The percentage of cells with >10 FANCD2 foci was determined. At least 300 nuclei were scored for each sample. Representative images are shown. All images were acquired at ×100 magnification. Graph represents average percentage of foci-positive cells from three independent experiments with standard deviation. *P< 0.05, Student's two-tailed t-test.