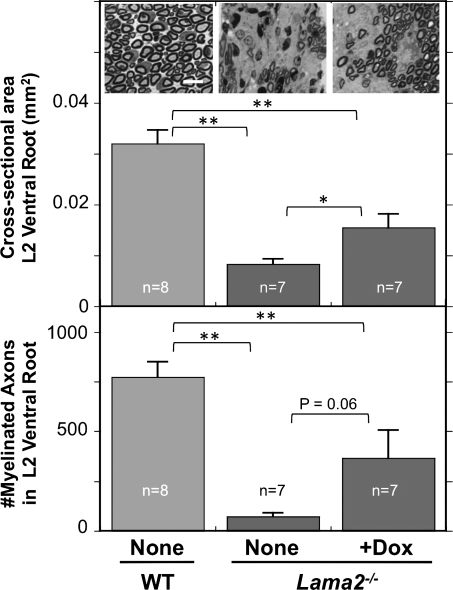
Figure 4.
Ventral roots of Lama2−/− mice were smaller and had fewer myelinated axons. Sections of L2 ventral roots from 4-week-old-untreated wild-type (WT and none, leftmost), untreated Lama2−/− (none, center) and doxycycline-treated Lama2−/− (+Dox, rightmost) mice were stained with toluidine blue and used to determine both the cross-sectional area (top) and the total number of myelinated axons in each ventral root (bottom). At 4 weeks of age, the L2 ventral roots from Lama2−/− mice were significantly smaller and had <10% as many myelinated axons as wild-type. Ventral roots from doxycycline-treated Lama2−/− mice were significantly larger than in untreated Lama2−/− mice, though still smaller than wild-type. Doxycycline treatment also increased the average number of myelinated axons in ventral roots from Lama2−/− mice, though this increase did not reach quite reach significance at P = 0.06 because three of the seven doxycycline-treated mice that were examined did not show improvement in ventral root pathology, sciatic nerve pathology or standup behavior (see text for details). Inset photos show representative sections of ventral roots from a wild-type mouse, an untreated Lama2−/− mouse and one of the four doxycycline-treated Lama2−/− mice in which axon number was increased; scale bar = 15 µm. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. Error bars = SE.