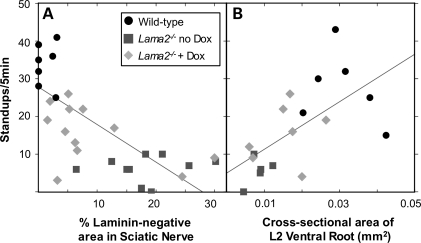
Figure 5.
Relationship between motor behavior and extent of pathology in sciatic nerves and ventral roots. Linear correlation analysis was used to examine the possible relationship of motor behavior measured by the standup assay (as in Fig. 1) with either (A) the extent of sciatic nerve pathology measured by area lacking laminin (as in Figs 2 and 3) or (B) the extent of ventral root pathology measured by the cross-sectional area (as in Fig. 4). Values from wild-type (circles), untreated Lama2−/− (squares) and doxycycline-treated Lama2−/− (diamonds) mice were plotted, and the linear correlation (line) was calculated for the total group. For (A), the correlation coefficient was r = 0.69 (P < 0.01); and for (B), r = 0.62 (P < 0.01). Both analyses indicated that standup behavior decreased with increased pathology. See text for additional discussion.