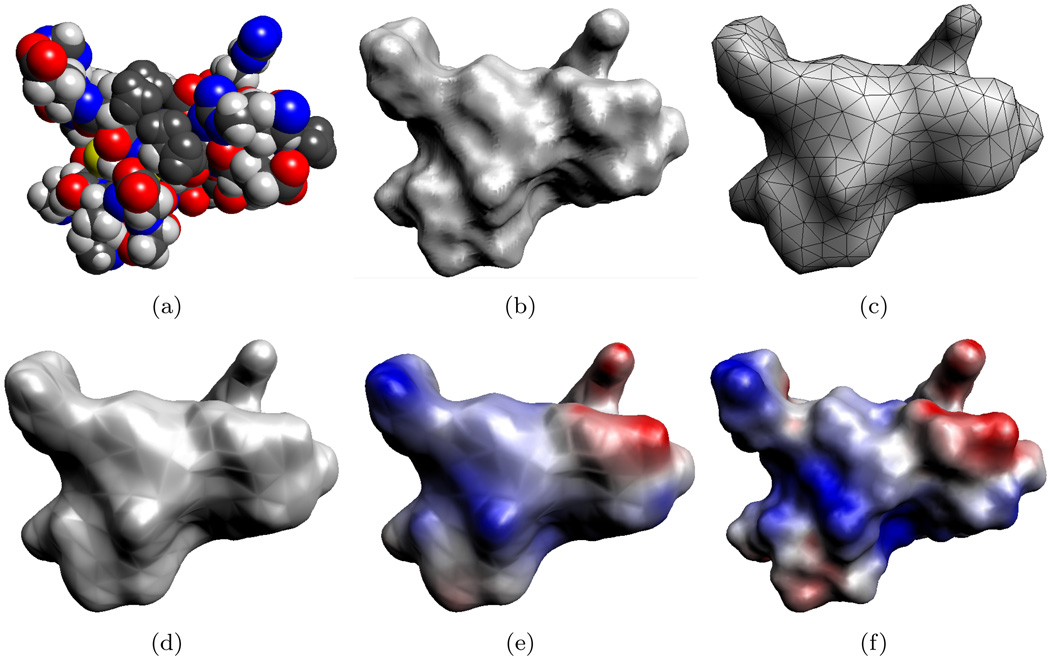
FIG. 4.1.
Molecular model of a protein (PDB id:1PPE, 436 atoms). (a) The van der Waals surface of the protein which models the molecule as a union of balls. (b) The variational molecular surface gives a smooth approximation of the van der Waals surface. (c) The variational surface is then triangulated and then decimated to produce a smaller mesh. This decimated mesh contains 1,000 triangles. (d) The algebraic spline molecular surface (ASMS) fits a smooth surface over the triangular mesh. (e) Electrostatic potential computed using the 1,000 patch ASMS. (f) Electrostatic potential using an ASMS with 74,812 patches. The surfaces in (e) and (f) are colored by the electrostatic potential, ranging from −3.8 kbT/ec (red) to +3.8 kbT/ec (blue).