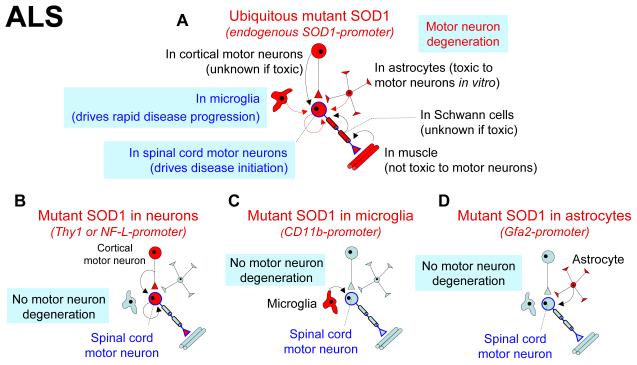
Figure 2.
Non-cell autonomous neurotoxicity in ALS. (a) Selective mutant SOD1 silencing demonstrated that mutant damage within motor neurons drives disease initiation8,22,23, while mutant expression within neighboring microglia underlies rapid disease progression7,8. The in vivo contributions of mutant SOD1 expression in astrocytes or Schwann cells are not yet established, while mutant expression in muscle does not contribute to disease56. Consistent with non-cell autonomous mechanisms, selective mutant expression in either motor neurons19,20 (b), astrocytes29 (c) or microglia7 (d) alone are not sufficient to induce motor neuron degeneration.