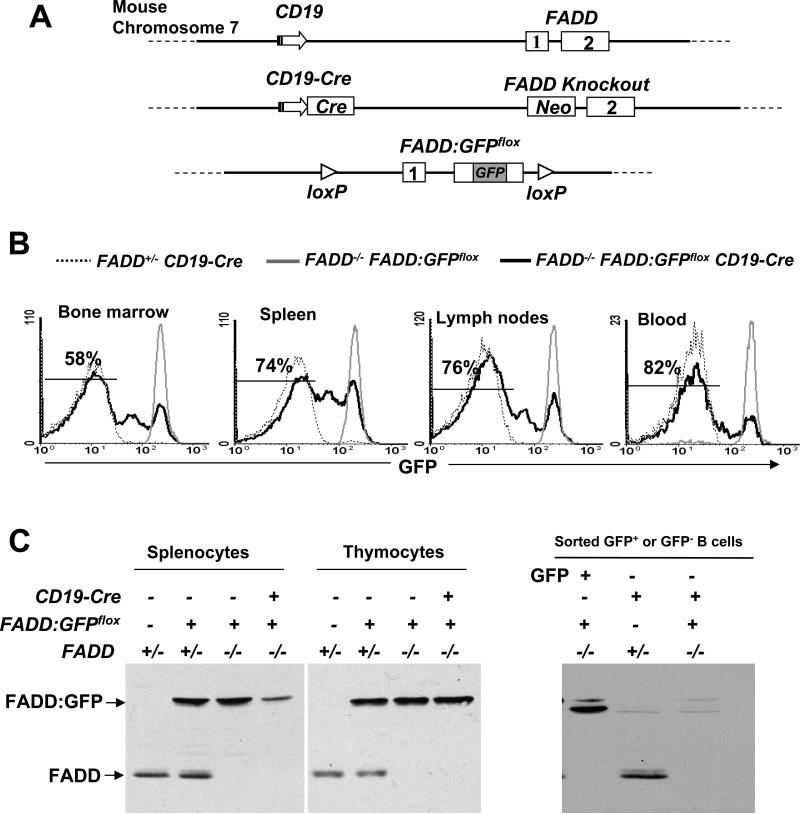
FIGURE 1.
(A) Diagrammatic scheme in generating B cell-specific FADD-/- mice. The CD19 locus is closely linked to FADD on mouse chromosome 7 with a ~10 centimorgan distance (top). The CD19-Cre allele (48) was crossed to the FADD knockout allele (22) (middle) by mouse mating in order to delete FADD:GFPflox specifically in B cells in FADD-/- mice. The promoter of CD19 (arrows), the neomycin-resistant gene (neo), exons of FADD (boxes) and GFP are indicated. Drawings are not to scale. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of FADD:GFP deletion in B cells. Single cell suspensions were prepared from the bone marrow, spleen, lymph nodes, and peripheral blood, and stained for CD19. The indicated percentages of GFP- cells in the CD19+ population of FADD-/- FADD:GFPflox CD19-Cre mice were determined by flow cytometry. Cells from FADD+/- CD19-Cre and FADD-/- FADD:GFPflox mice were used as GFP- and GFP+ controls, respectively. Histograms are from one experiment using one mouse of each genotype, and are representative of 14 independent experiments. (C) Total thymocytes and splenocytes (left) or sorted GFP- B cells (right) from FADD-/- FADD:GFPflox CD19-Cre mice were analyzed by western blotting using anti-FADD antibodies. FADD+/-, FADD+/- FADD:GFPflox, FADD-/- FADD:GFPflox, FADD+/- FADD:GFPflox CD19-Cre mice were used as controls. The absence of FADD:GFP in GFP- cells were confirmed in three independent experiments.