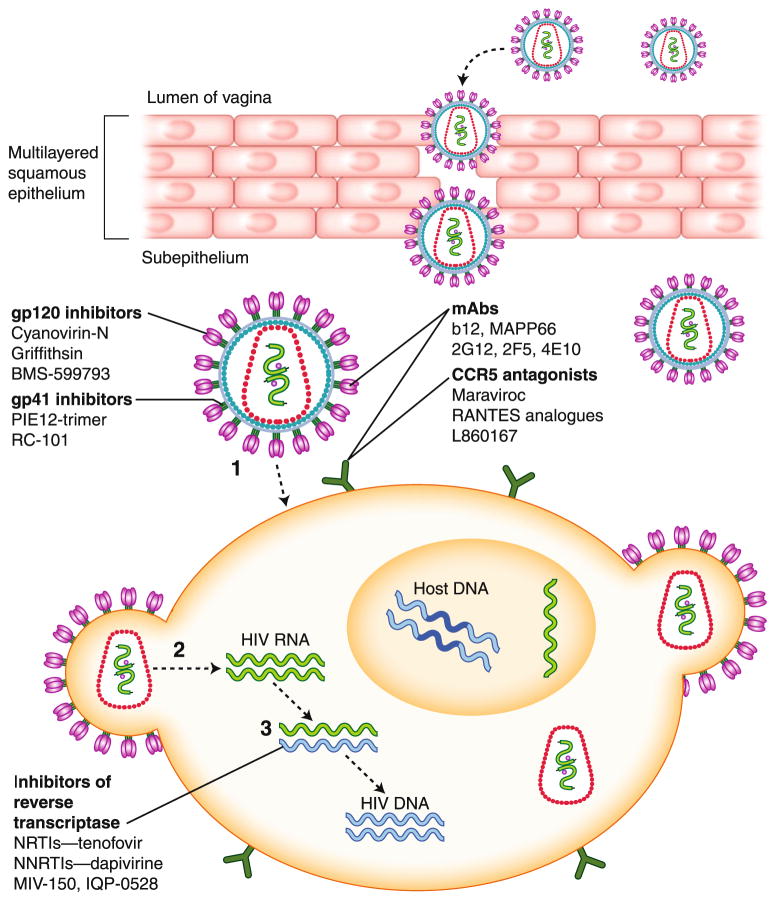
Fig. 1.
Antiretroviral (ARV) microbicides and mechanism of action within the female genital tract. ARVs inhibit HIV infection of target cells at various steps including viral attachment (1), fusion (2), and reverse transcription (3). CCR5, chemokine (C–C) motif receptor 5; mAbs, monoclonal antibodies; NNRTI, nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor; NRTI, nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor; RANTES, regulated upon activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted