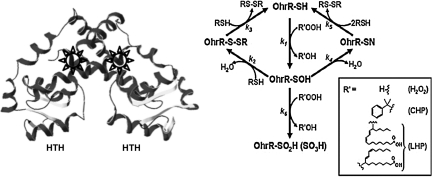
FIG. 2.
BSH covalently modifies the B. subtilis OhrR repressor. OhrR (organic hydroperoxide-resistance repressor) is a dimeric, DNA-binding protein with a helix-turn-helix (HTH) DNA-binding motif. The active site for oxidation (Cys15) is located in the amino-terminal α-helix of each monomer (star). In B. subtilis, no other Cys residues exist in the protein (it is a member of the 1-Cys OhrR family), and oxidation of the protein (OhrR-SH; right) by various organic peroxides (R'-OOH; see inset legend) leads initially to the protein sulfenic acid (OhrR-SOH), which retains DNA-binding activity. Subsequent modifications inactivate the protein by (a) formation of mixed disulfides with LMW thiols (k2), (b) overoxidation to the sulfinic and sulfonic acids (k6), or (c) condensation with a backbone amide to generate a sulfenamide (k4) (adapted from 61). In B. subtilis, BSH was detected by virtue of its ability to form an OhrR-S-SB mixed disulfide in vivo (32).