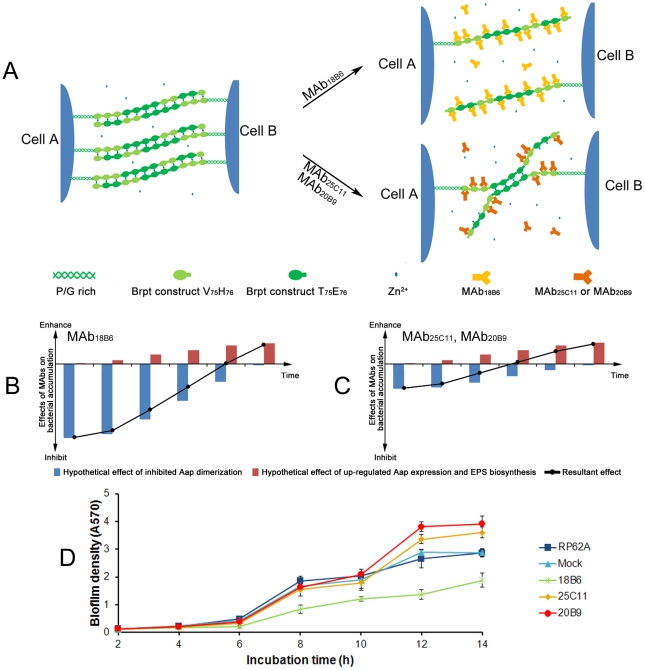
Figure 10. Contradictory actions of the MAbs on biofilm formation.
(A) Model for MAbs affecting Aap dimerization. According to the zinc zipper model for intercellular adhesion mediated by zinc-dependent Aap dimerization [22], we speculate that MAb18B6 binds to all twelve AapBrpt constructs and significantly inhibits Aap dimerization, whereas MAb25C11 and MAb20B9 bind to six of the AapBrpt constructs and block Aap dimerization incompletely. (B, C) Model for MAbs affecting bacterial accumulation. The resultant effect (black curves) of the MAbs on bacterial accumulation is attributed to the counteraction between two contradictory actions, one inhibits biofilm formation by binding to Aap (blue bars), and the other enhances bacterial accumulation by up-regulating Aap expression and EPS biosynthesis (red bars). (D) Kinetic studies on biofilm formation. The cells of S. epidermidis RP62A were co-cultured with 10 µg/mL of each MAb in 96-well polystyrene plates initially at 4°C for 2 h, and then at 37°C for 2 h, 4 h, 6 h, 8 h, 10 h, 12 h, and 14 h, respectively. After incubation, biofilm formation at different time points was measured using crystal violet staining, and the results are depicted as means ± SD of three independent experiments.