Fig. 4.
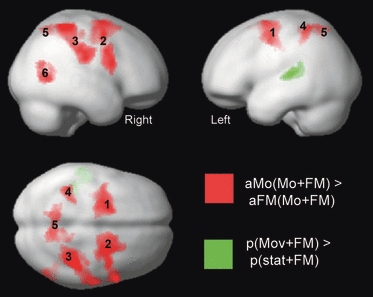
Scope of the network of brain regions engaged when participants are attending to stimulus motion as compared with attending to FM (red). In both conditions, the stimulus is the same. The locations of the differential activity are contrasted with the position of the passive motion localizer (green). This figure clearly illustrates how the motion-related task differences engage higher-level regions, whereas the motion-sensitive response is restricted to the auditory cortex.
