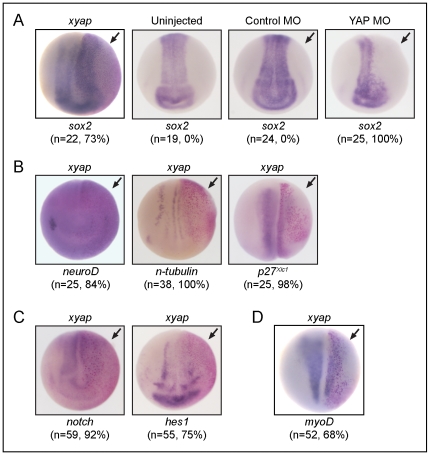
Figure 4. xYAP gain-of-function expands neural progenitor fields, while neural differentiation is inhibited.
(A) The neural plate progenitor field marked by sox2 expression (blue stain) was darker, longer, and/or wider on the xYAP-injected side (arrow, red β-gal staining) compared to the uninjected side of the same embryo. xYAP MO-mediated knockdown (40 ng) eliminated sox2 expression on the injected side, whereas a control MO (cMO) did not. In this and all subsequent panels: n = sample size; % = frequency of the phenotype; arrow indicates injected side. (B) Three genes indicative of neural differentiation (neuroD, n-tubulin, p27Xic1) were inhibited by xYAP gain-of-function. (C) xYAP gain-of-function reduced notch and hes1 expression. (D) Muscle differentiation marker, myoD, was reduced by xYAP gain-of-function. All views are dorsal-anterior.